• Up to 4 types have been described: • Recto-urethral fistula: this rare abnormality is usually associated with an imperforate anus • Urethral duplication: there is usually complete duplication with one of the urethras ending as a hypospadias • Hypospadias: absence of the ventral aspect of the distal urethra • Epispadias: absence of the dorsal aspect of the distal urethra
Urethra
URETHRA: BENIGN DISORDERS
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
Clinical presentation
 Type 1 (the most common): two mucosal folds at the level of the verumontanum with a ventral central slit-like orifice
Type 1 (the most common): two mucosal folds at the level of the verumontanum with a ventral central slit-like orifice
 Type 3: this has a pin-point, eccentric orifice which results in forward ballooning of the valve, giving a ‘wind in the sail’ appearance on an oblique MCUG projection
Type 3: this has a pin-point, eccentric orifice which results in forward ballooning of the valve, giving a ‘wind in the sail’ appearance on an oblique MCUG projection  there is a high association with renal dysplasia and minimal upper tract dilatation
there is a high association with renal dysplasia and minimal upper tract dilatation
Other urethral anomalies
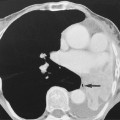
 air within the bladder confirms the diagnosis
air within the bladder confirms the diagnosis
Urethra

 incomplete obliteration may lead to the formation of cysts between the bladder and rectum which can present with urinary frequency or obstructive symptoms
incomplete obliteration may lead to the formation of cysts between the bladder and rectum which can present with urinary frequency or obstructive symptoms it is often associated with maldevelopment of the genitalia
it is often associated with maldevelopment of the genitalia they are located near the distal verumontanum and result from the abnormal migration of mucosal folds (Wolffian duct remnants) from the verumontanum to the membranous urethra
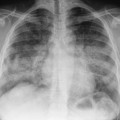
they are located near the distal verumontanum and result from the abnormal migration of mucosal folds (Wolffian duct remnants) from the verumontanum to the membranous urethra progressive oligohydramnios during pregnancy (± pulmonary hypoplasia)
progressive oligohydramnios during pregnancy (± pulmonary hypoplasia)  obstructive symptoms
obstructive symptoms  infection
infection  haematuria
haematuria there may be dilatation of the posterior uretha proximal to the valve
there may be dilatation of the posterior uretha proximal to the valve  vesicoureteric reflux may be present (and is associated with poor renal function on the affected side)
vesicoureteric reflux may be present (and is associated with poor renal function on the affected side) infection
infection  carcinoma
carcinoma increased urinary frequency
increased urinary frequency  dysuria
dysuria  dyspareunia
dyspareunia it usually has a short neck
it usually has a short neck Ureaplasma urealyticum
Ureaplasma urealyticum  tuberculosis
tuberculosis  schistosomiasis
schistosomiasis strictures
strictures  reflux into the glands of Littre, Cowper’s gland ducts, prostatic ducts and seminal vesicles
reflux into the glands of Littre, Cowper’s gland ducts, prostatic ducts and seminal vesicles  pseudodiverticulae
pseudodiverticulae there is proximal dilatation and it classically follows a gonococcal urethritis
there is proximal dilatation and it classically follows a gonococcal urethritis