Chapter 20 Vertebral Augmentation (Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty), Transpedicular Approach
Although alternative techniques have been described, the approach described here involves the use of a trajectory view as the primary approach. The vertebral body is cannulated in the trajectory view (see Appendix 1). Figure 20–10, E, demonstrates the angulation of the needle trajectory in the lateral view with various fracture-pattern scenarios.
A key operational difference between kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty lies in the placement of the working cannula. During a kyphoplasty procedure, when the osteo introducer anchors 1 to 2 mm ventral to the posterior vertebral body (see Figure 20–3, A), a biopsy can be taken; alternatively, the drill can be used to create a path for the balloon tamp (see Figure 20–10, A and B). During vertebroplasty, the introducer cannula is driven from the pedicle toward the midline of the vertebral bone without additional instrumentation. When the tip of the cannula has docked into the posterior vertebral body (see Figure 20–3, A), the visualization of the tip medial to the pedicle is expected in the anteroposterior view; however, advancement should always be done in the lateral view to protect the great vessels.
The oblique transpedicular view is identical to the trajectory view (see Figure 20–1), as described previously.
Note: Please see page ii for a list of anatomical terms/abbreviations used in this book.
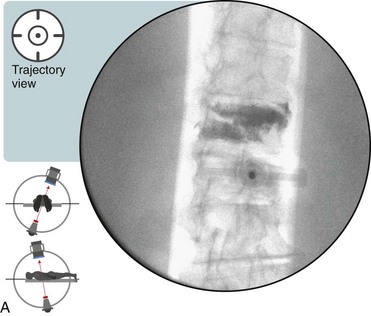
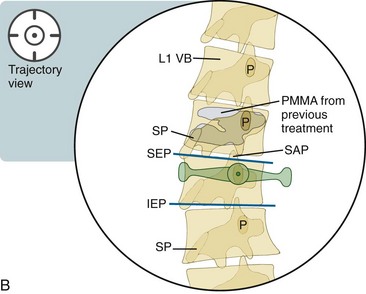
 Transpedicular Advancement: Trajectory View (Figure 20–1)
Transpedicular Advancement: Trajectory View (Figure 20–1)
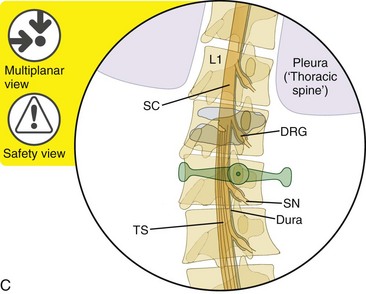
![]() Trajectory View Safety Considerations
Trajectory View Safety Considerations
 Avoid the spinal cord and the dural sac contents by staying lateral to the medial border of the pedicle.
Avoid the spinal cord and the dural sac contents by staying lateral to the medial border of the pedicle.
 Avoid the superior and inferior nerve roots and the spinal nerves by staying within the inferior and superior pedicular borders.
Avoid the superior and inferior nerve roots and the spinal nerves by staying within the inferior and superior pedicular borders.
 Avoid pneumothorax during thoracic vertebral body augmentation by avoiding the violation of the lateral wall of the vertebral body by traversing in a lateral-to-medial intrapedicular pathway.
Avoid pneumothorax during thoracic vertebral body augmentation by avoiding the violation of the lateral wall of the vertebral body by traversing in a lateral-to-medial intrapedicular pathway.
 Confirm the level (with the anteroposterior view).
Confirm the level (with the anteroposterior view).
 Tilt the C-arm to line up the inferior endplate of the vertebral body to be treated.
Tilt the C-arm to line up the inferior endplate of the vertebral body to be treated.
 Ipsilateral oblique approximately 10 to 20 degrees ipsilateral so that the pedicle appears as a clock face.
Ipsilateral oblique approximately 10 to 20 degrees ipsilateral so that the pedicle appears as a clock face.
 Position the pedicle in the oblique view so that it is completely encased in the outline of the vertebral body.
Position the pedicle in the oblique view so that it is completely encased in the outline of the vertebral body.
 The transpedicular entry point is the superior lateral quadrant (i.e., the 10 or 2 o’clock position, respectively, for left or right entry) for fractures occuring along the superior endplate (majority of fractures).
The transpedicular entry point is the superior lateral quadrant (i.e., the 10 or 2 o’clock position, respectively, for left or right entry) for fractures occuring along the superior endplate (majority of fractures).
 Anesthetize the needle tract and periosteum overlying the pedicle.
Anesthetize the needle tract and periosteum overlying the pedicle.
 Nick the skin (No. 11 blade for kyphoplasty or an 18-gauge needle for vertebroplasty).
Nick the skin (No. 11 blade for kyphoplasty or an 18-gauge needle for vertebroplasty).
 Insert the osteo introducer device or the bone needle, and place the tip onto the pedicle.
Insert the osteo introducer device or the bone needle, and place the tip onto the pedicle.
 Gently tap the bone needle with a mallet to create a starting hole.
Gently tap the bone needle with a mallet to create a starting hole.
 Advance the needle with gentle manual pressure or mallet tapping.
Advance the needle with gentle manual pressure or mallet tapping.