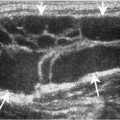
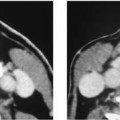
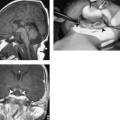
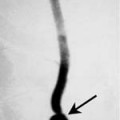
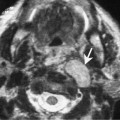
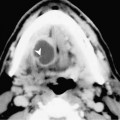
Chapter 100 Wegener’s granulomatosis is a granulomatous vasculitis. The etiology is unknown but may be immunologically mediated. It is characterized by three specific criteria: necrotizing granulomas with vasculitis of the upper and lower respiratory tracts, systemic vasculitis, and focal necrotizing glomerulitis. There is a limited form of this disease that involves the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, or both. However, the limited form does not involve the kidneys, or the respiratory involvement precedes the renal involvement by a long interval. Laryngeal involvement usually occurs as subglottic narrowing or stenosis. Of 158 patients treated at the National Institutes of Health, over 90% had otolaryngologic abnormalities and 16% had subglottic stenosis. The incidence of subglottic stenosis appears to be increased in patients under the age of 20. Patients with laryngeal involvement usually present with sore throat and laryngitis. Occasionally, the subglottic stenosis may progress and require tracheostomy. Because Wegener’s is a systemic disease, other symptoms are common and include fever, arthralgia, sinusitis, otitis media, and saddle-nose deformity. Patients with laryngeal involvement typically have or will soon develop widespread pulmonary involvement (Fig. 100–1).
Wegener’s Granulomatosis of the Larynx
Epidemiology
Clinical Findings
Pathology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree