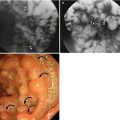
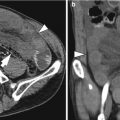
Fig. 9.1
Partial gastrectomy with B-I anastomosis. (a) UGIS depicts B-I gastroduodenostomy (arrowheads). (b, c) Axial CT images show distal gastrectomy with gastroduodenostomy (Billroth I procedure); the connection between the stomach and duodenum is an end-to-end anastomosis (arrowheads) using the entire free edge of the stomach (Polya procedure)
9.4.2 Partial Gastrectomy with B-II Anastomosis
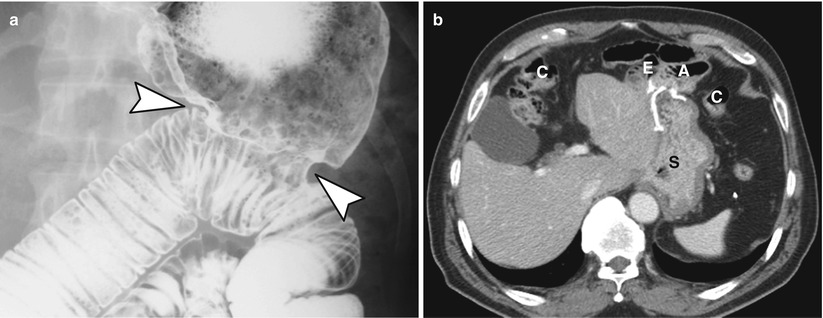
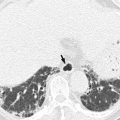
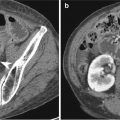
Fig. 9.2
Partial gastrectomy with B-II anastomosis. (a) UGIS demonstrates B-II gastrojejunostomy with bilateral plication deformity (arrowheads) which was caused by oversewn suture at the GJ anastomosis area. (b) Axial CT image shows antecolic gastrojejunostomy and the relationship between the remnant stomach, colon, and afferent and efferent loops. A afferent loop, E efferent loop, S stomach, C colon
9.4.3 Partial Gastrectomy with Braun Anastomosis
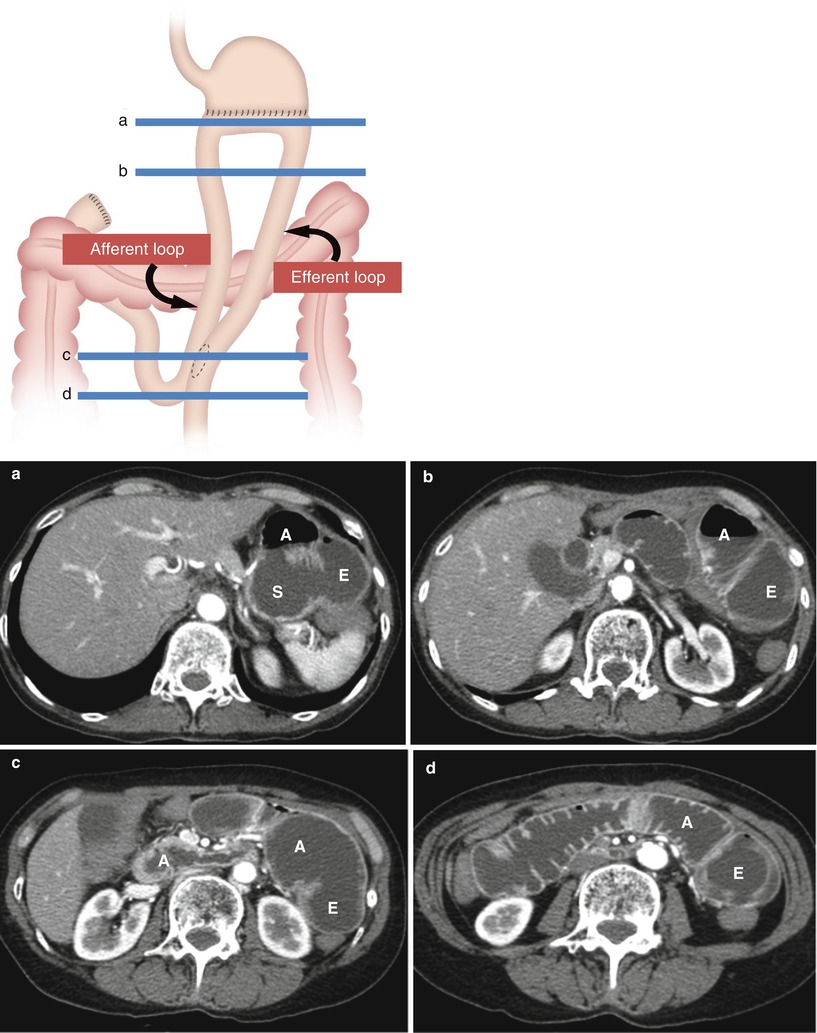
Fig. 9.3
Illustrated diagram describes subtotal gastrectomy with braun anastomosis. (a–d) Serial axial CT images obtained at each level of Braun anastomosis well demonstrate the relationship between the remnant stomach (S) and the course of afferent and efferent loops with fluid distension. A afferent loop, E efferent loop
9.4.4 Proximal Gastrectomy with EJ Stomy
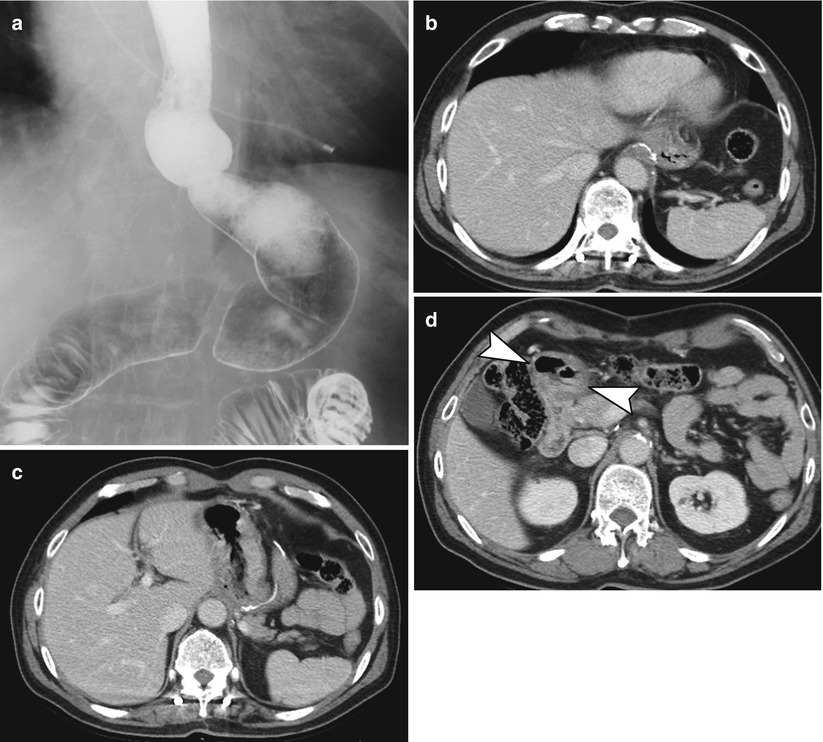
Fig. 9.4
Proximal gastrectomy with EJ stomy. (a–d) UGIS (a) and axial CT scans (b–d) depict the postoperative anatomy of proximal gastrectomy with EJ stomy. Intact pylorus is observed (arrowheads in d)
9.4.5 Total Gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y Anastomosis
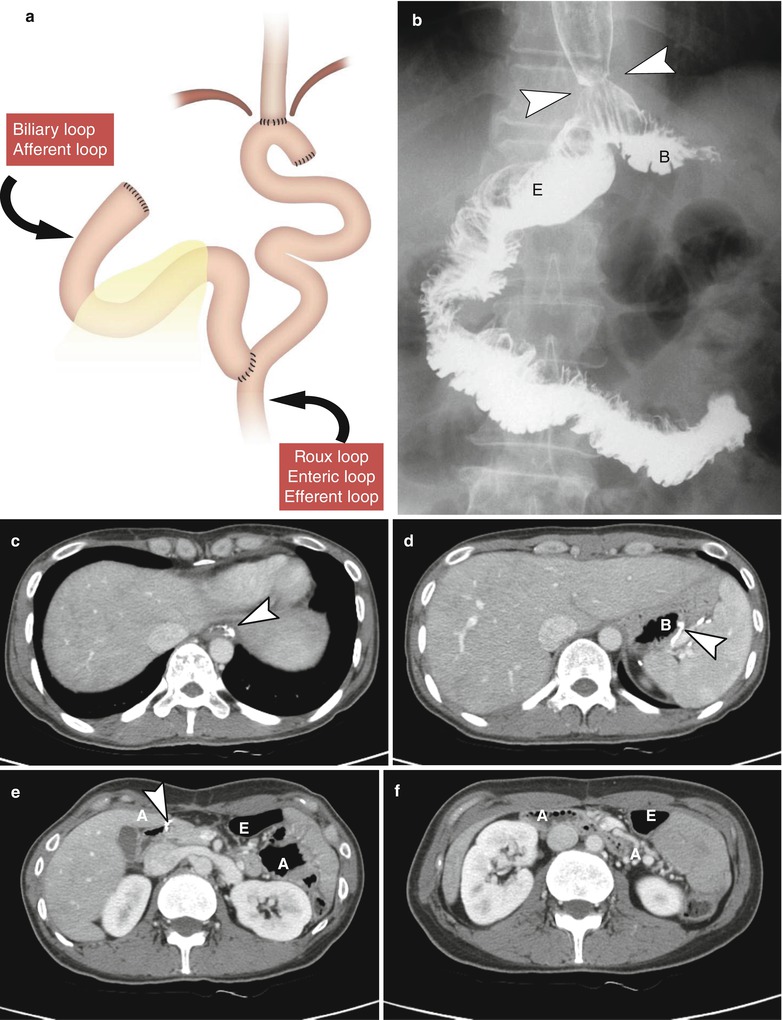
Fig. 9.5
Total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y anastomosis. (a) Diagram of total gastrectomy with EJ stomy, JJ stomy. (b) UGIS demonstrates the postoperative anatomy of total gastrectomy with EJ stomy (arrowheads) and Roux-en-Y anastomosis. (c–f) Axial CT scans shows postoperative anatomy of total gastrectomy at different section levels. Note the radiopaque suture materials (arrowheads) at EJ stomy (c), blind pouch (B in d), and distal end of afferent loop (A in e). B blind pouch, A afferent loop, E efferent loop
9.4.6 Pylorus-Preserving Gastrectomy with B-I Anastomosis
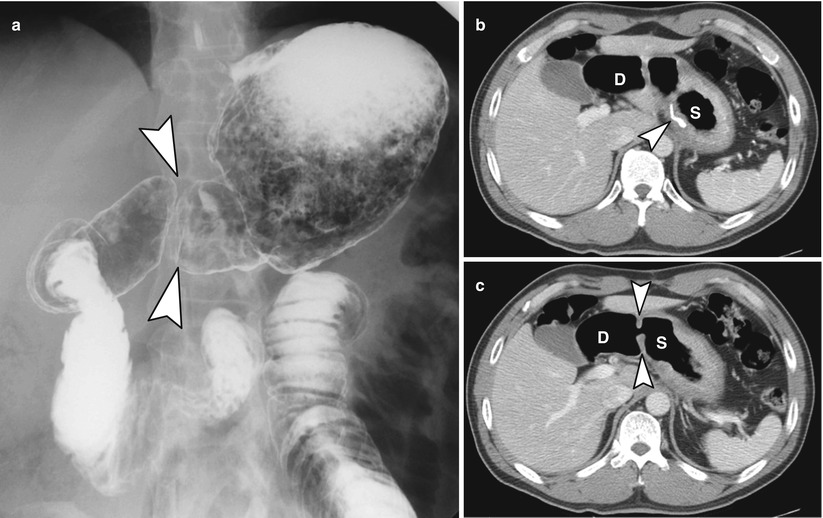
Fig. 9.6
Pylorus-preserving gastrectomy with B-I anastomosis. (a) UGIS of pylorus-preserving gastrectomy with B-I anastomosis. Note intact pylorus (arrowheads). (b, c) Axial CT scans depict suture materials of lesser curvature side (arrowhead in b) and intact pylorus (arrowheads in c). S remnant stomach, D duodenum
9.4.7 Normal Postoperative Findings
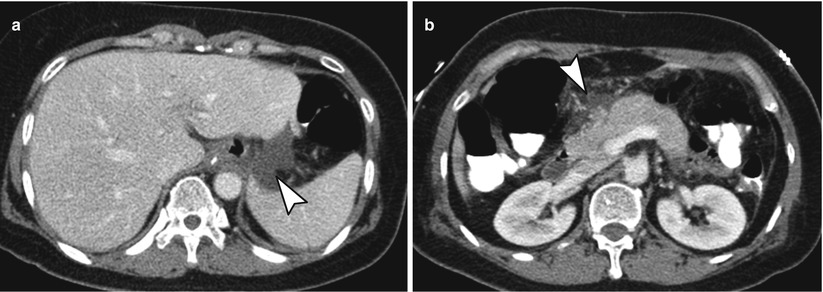
Fig. 9.7
Normal postoperative findings. (a, b) Axial CT images demonstrate small amount of postoperative fluid without complication around anastomotic site (arrowhead) (a), duodenal stump or peripancreatic area (arrowhead) (b)
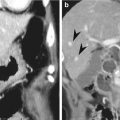
9.4.8 Anastomotic Leakage at EJ Stomy Induced Small Abscess in Lesser Sac
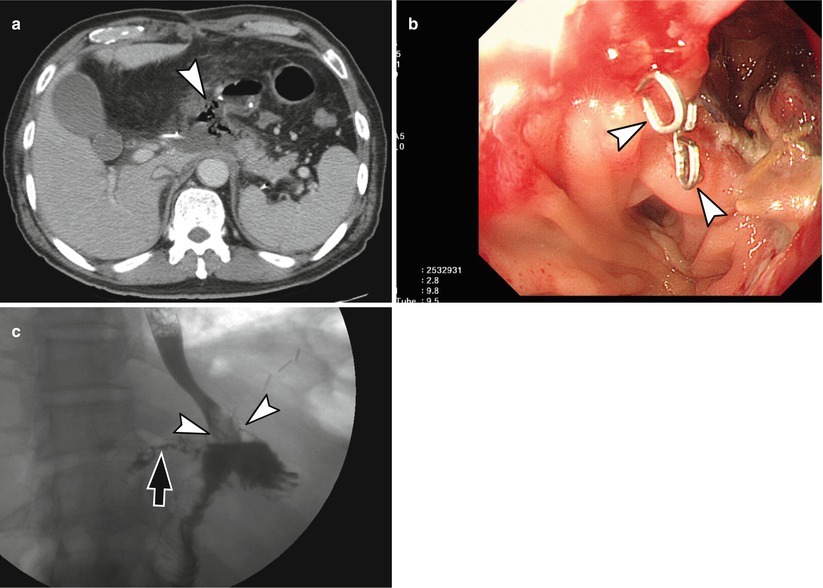
Fig. 9.8
Anastomotic leakage at EJ stomy induced small abscess in lesser sac. A 67-year-old man who had undergone total gastrectomy visited the emergency room for epigastric pain. (a) CT scan obtained 2 weeks after surgery shows an extraluminal air bubbles and small amount of fluid accumulation (arrowhead) posterior to EJ stomy site. (b) Endoscopy reveals disrupted suture staples (arrowheads) and defect at anastomotic suture line. (c) UGIS obtained after oral intake of Gastrografin reveals contrast leakage (arrow) at EJ anastomosis site (arrowheads)
9.4.9 Anastomotic Leakage at EJ Stomy Induced Large Abscess Cavity in Left Subphrenic Area
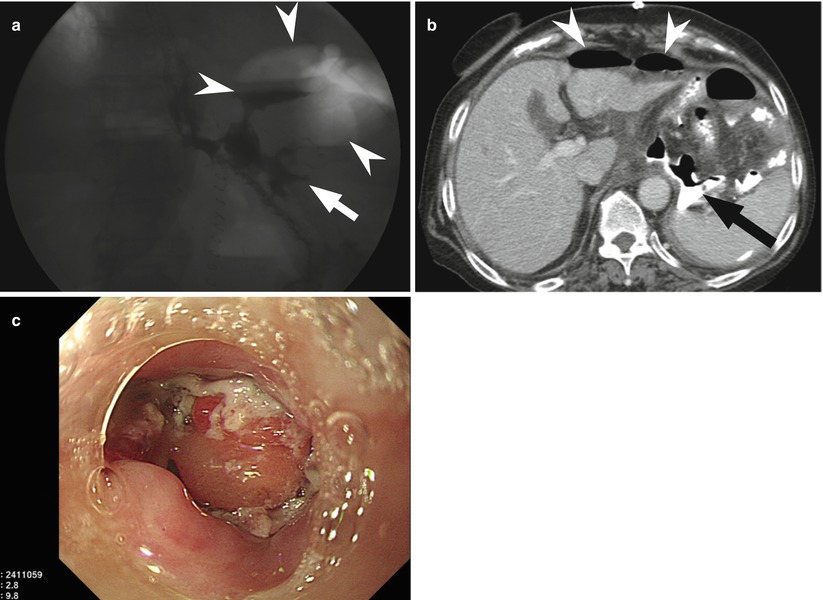
Fig. 9.9
Anastomotic leakage at EJ stomy induced large abscess cavity in left subphrenic area. A 77-year-old woman had undergone total gastrectomy complained fever at postoperative day 4. (a) Spot image from UGIS with water-soluble contrast agent shows focal leak (arrow) from left lateral aspect of esophagojejunal anastomosis into large gas-containing extraluminal collection (arrowheads) in left subphrenic space. (b) CT obtained immediately after UGIS demonstrates contrast material leakage to left subphrenic area (arrow) and pneumoperitoneum (arrowheads). (c) Endoscopy reveals extraluminal abscess cavity containing pus
9.4.10 Anastomotic Dehiscence at Gastrogastrostomy Along Lesser Curvature
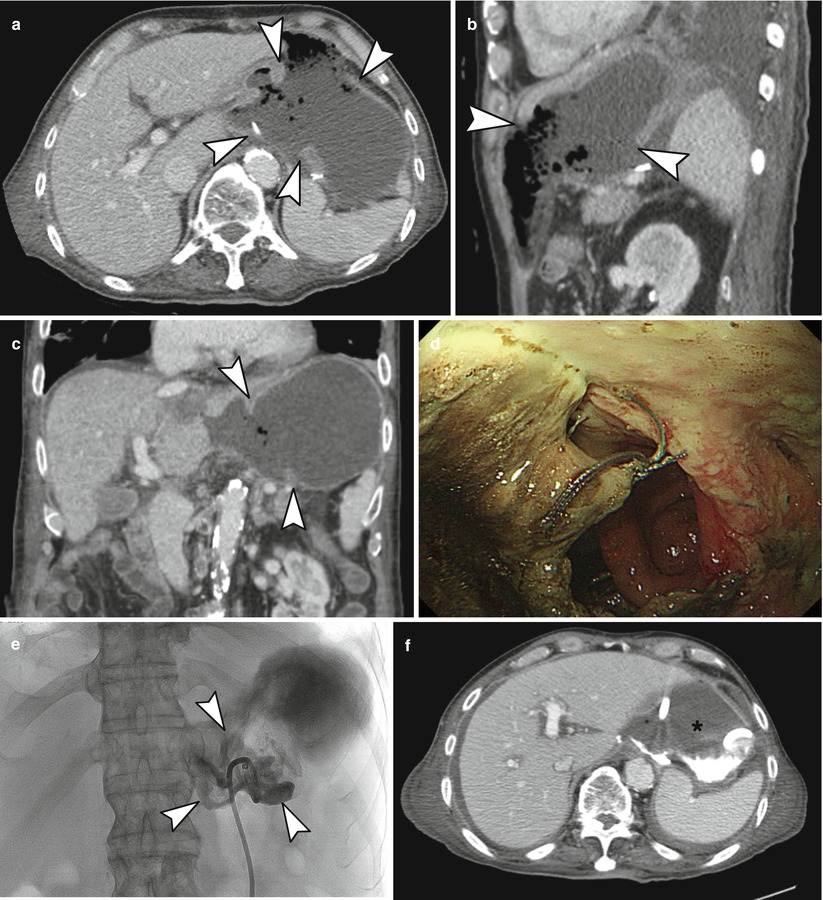
Fig. 9.10
Anastomotic dehiscence at gastrogastrostomy along lesser curvature. A 76-year-old man who had undergone laparoscopy-assisted pylorus-preserving gastrectomy for EGC complained melena at postoperative day 16. (a–c) Axial (a), sagittal (b), and coronal (c) CT images demonstrate wide disruption of suture line along lesser curvature of gastrogastrostomy (arrowheads). The remnant gastric lumen is fully open to peritoneal cavity. (d) Endoscopy reveals disrupted suture line, and the scope was directly passed to pus-covered peritoneal cavity. (e) Abscessogram obtained with administration of contrast material through the drainage catheter demonstrates extensive contrast leak to the peritoneal cavity (arrowheads). (f) CT taken after abscessogram depicts contrast retain in the large abscess cavity formed by remnant gastric wall and peritoneum
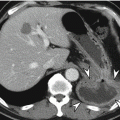
9.4.11 Small Leak from Duodenal Stump
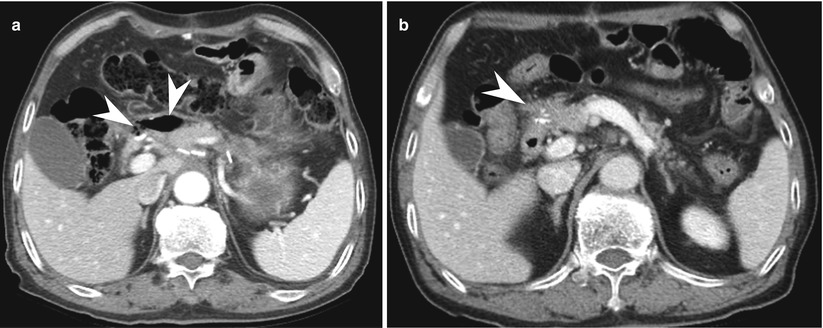
Fig. 9.11




Small leakage from duodenal stump. A 76-year-old man who had undergone laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy for EGC visited ER due to epigastric pain and vomiting at postoperative day 22. (a) CT reveals small amount of pneumoperitoneum with air bubbles and thick wall formation (arrowheads) anterior to duodenal stump area. (b) After he had been prescribed antibiotics and kept NPO state for 1 week, follow-up CT shows complete resolution of complicated fluid and air. NPO no per oral intake
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree