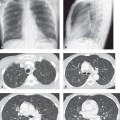
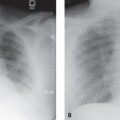
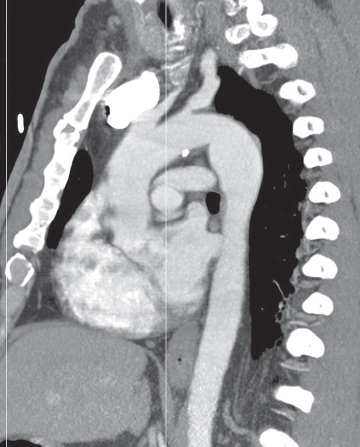
CASE 101 46-year-old man involved in a MVC with a clinical concern of hemomediastinum and potential acute traumatic aortic injury Contrast-enhanced sagittal oblique MIP CT (mediastinal window) (Fig. 101.1) demonstrates a focal convex bulge in the aortic isthmus consistent with a Type III ductus diverticulum. Note the smooth contour and obtuse margin formed with the aortic lumen and the absence of an intimal flap and hemomediastinum. Type III Ductus Diverticulum None The increased use of MDCT has led to the recognition of numerous vascular variants that may mimic acute aortic injuries. The most common variants include typical ductus diverticulum, atypical ductus diverticulum, aortic spindle, and branch vessel infundibula. Fig. 101.1 Type I— concave contour Type II— mild straightening or convexity without a discrete bulge Type III—discrete focal bulge referred to as the ductus diverticulum (Fig. 101.1) Atypical ductus diverticulum—often causes even more diagnostic confusion; characterized superiorly by a shorter, steeper slope and inferiorly by a more typical, gentler slope (Fig. 101.2) Aortic spindle
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree