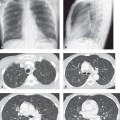
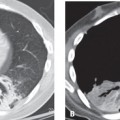
CASE 104 50-year-old woman with persistent fever, progressive dyspnea, and non-productive cough for several weeks despite antibiotics for presumed community-acquired pneumonia Baseline frontal chest X-ray (Fig. 104.1A) reveals mild hypoaeration but is otherwise unremarkable. Follow-up chest X-ray eight days later (Fig. 104.1B) shows bilateral, patchy ground glass and subtle reticular opacities. The heart is not enlarged. Lung volumes remain mildly diminished. Chest CT (lung window) through the upper (Fig. 104.1C), mid (Figs. 104.1D, 104.1E), and lower (Figs. 104.1E, 104.1F) lung zones performed two days later demonstrates bilateral ground glass opacities with sparing of some secondary pulmonary lobules, resulting in a geographic appearance to the lungs. Smooth septal thickening, intralobular lines, and ground glass result in a “crazy paving” pattern. Mild bronchial dilatation is present. Patient required mechanical ventilator support two days later. Subsequent open lung biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. Acute Interstitial Pneumonia (AIP) • Permeability Edema • Diffuse Pneumonia • Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage • Acute Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis The idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP) are the most common group of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases. They were recently reclassified by a multidisciplinary panel of experts in a collaborative effort by the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS), and the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP). The new classification includes seven distinct clinico-pathologic entities: (1) idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA); (2) non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP); (3) cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP); (4) acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP); (5) lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP); (6) respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD); and (7) desquamative interstitial pneumonitis (DIP). Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree