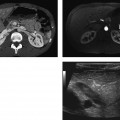
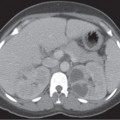
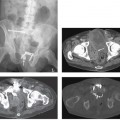
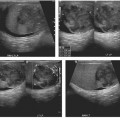
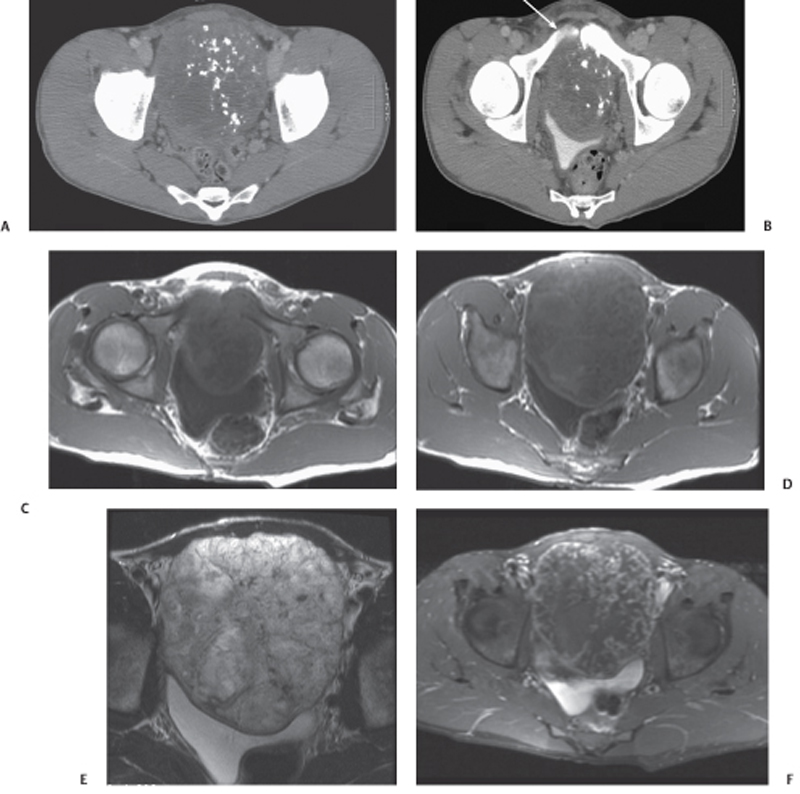
CASE 105 A 28-year-old man presents with a relatively short history of constipation and urinary problems. Fig. 105.1 (A,B) Axial contrast-enhanced CT images demonstrate a large low-attenuation mass with coarse central calcifications located anterior to the urinary bladder. A subtle cortical defect is present in the left pubic symphysis where the mass abuts it (arrow). (C,D) Axial T1-weighted MR images demonstrate a large T1 hypointense mass causing mass effect on the urinary bladder. (E) The mass is heterogeneously bright on an axial T2 sequence and (F) demonstrates heterogeneous, predominantly peripheral enhancement on the fat-suppressed T1 postcontrast image. An axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan (Fig. 105.1A,B) demonstrates a large low-attenuation mass with coarse central calcifications located anterior to the urinary bladder. A subtle cortical defect is present in the left pubic symphysis where the mass abuts it. Axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images (Fig. 105.1C,D) demonstrate a large T1 hypointense mass causing mass effect on the urinary bladder. The mass is heterogeneously bright on an axial T2 sequence and demonstrates heterogeneous, predominantly peripheral enhancement on the fat-suppressed T1 postcontrast image (Fig. 105.1E,F).
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree