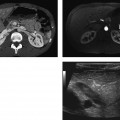
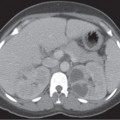
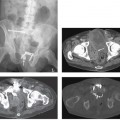
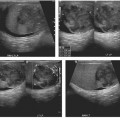
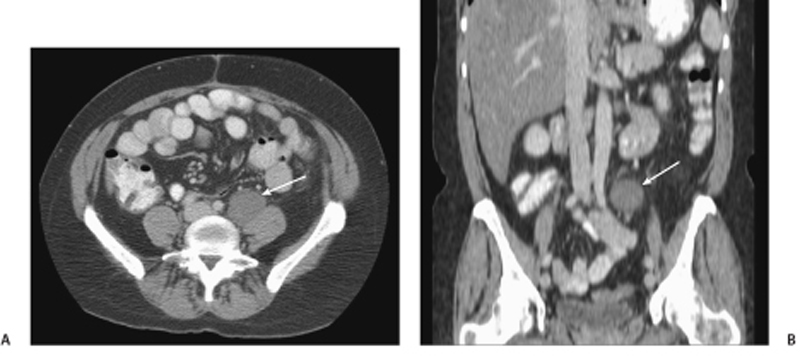
CASE 107 A 46-year-old woman presents with a history of retroperitoneal liposarcoma status postresection. Fig. 107.1 (A) Axial and (B) coronal contrast-enhanced CT images show a rounded, relatively homogeneous mass that measures water density by Hounsfield units in the retroperitoneal region adjacent to the left psoas muscle (arrow). Axial and coronal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) images show a rounded, relatively homogeneous mass that measures water density by Hounsfield units in the retroperitoneal region adjacent to the left psoas muscle (Fig. 107.1). Metastatic liposarcoma with pseudocystic sign Liposarcoma is a malignancy of adipose cells. It is the most common primary retroperitoneal tumor and the second most common soft tissue sarcoma in adults. Liposarcomas make up 95% of all fatty retroperitoneal tumors. They are usually seen in patients ages 40 to 60 years and occur more commonly in men than in women.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree