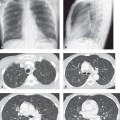
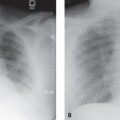
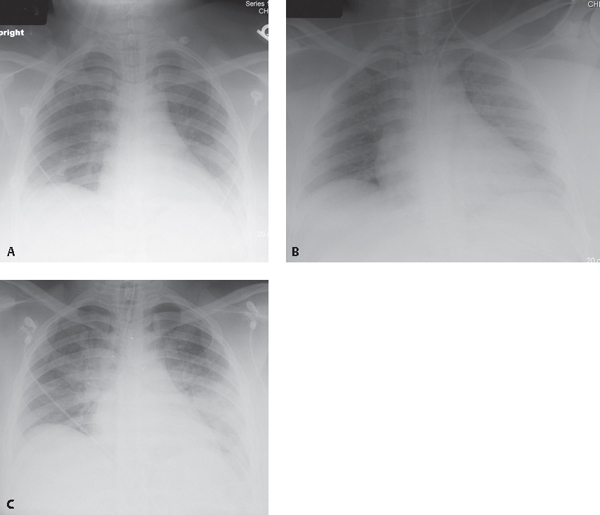
CASE 132 21-year-old woman who developed severe laryngospasm following extubation, necessitating reintubation AP chest radiograph (Fig. 132.1A) acquired six hours before extubation shows an appropriately positioned endotracheal tube, slight decrease in vascular clarity, and mild basilar hypoaeration. AP chest radiograph (Fig. 132.1B) acquired roughly 20 minutes following the onset of post-extubation laryngospasm reveals slightly diminished but largely unchanged vascular clarity and basilar hypoaeration. AP chest exam (Fig. 132.1C) obtained 30 minutes following reintubatation and subsequent relief of the laryngospasm demonstrates significant decrease in vascular clarity and central, perihilar ground glass opacities, right greater than left, consistent with pulmonary edema. Fig. 132.1 Post-Obstructive (Negative Pressure) Pulmonary Edema • Increased Hydrostatic Pressure Pulmonary Edema of Other Etiologies • Aspiration Post-obstructive negative pressure pulmonary edema (NPPE) is a mixed form of edema (see discussion in Case 131
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree