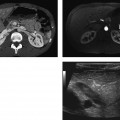
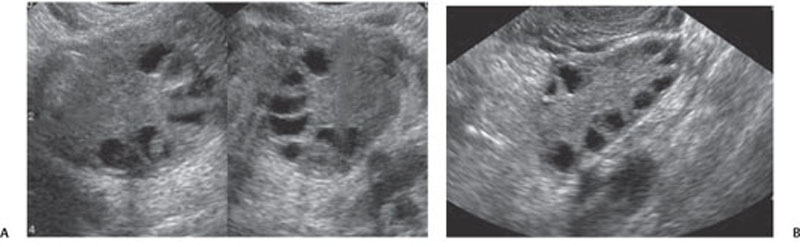
CASE 133 A 27-year-old woman presents with secondary amenorrhea, hirsutism, and obesity. Fig. 133.1 (A,B) Transvaginal ultrasound images demonstrate enlargement of the ovaries with multiple, small, peripherally located hypoechoic follicles and slightly increased echogenicity of the central stroma. Transvaginal ultrasound images (Fig. 133.1) demonstrate enlargement of the ovaries with multiple, small, peripherally located hypoechoic follicles and slightly increased echogenicity of the central stroma. Polycystic ovary syndrome (POS) Polycystic ovary syndrome, also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is one of the most common endocrine disorders occurring in women of reproductive age (4–12%). This condition is characterized by chronic anovulation, presumably associated with hypothalamic pituitary dysfunction, which leads to abnormalities in the metabolism of both estrogen and androgens. At pathology, the ovaries are enlarged and sclerotic, with multiple atretic peripherally located follicles and a thickened external capsule due to hyperplasia of the theca stromal cells. Patients typically present with infertility, menstrual abnormalities such as oligomenorrhea (menstrual bleeding occurring at longer interval) or secondary amenorrhea (absence of menses for more than 6 consecutive months), dysfunctional vaginal bleeding, hirsutism, and obesity. Minor findings are sleep apnea, acanthosis nigricans (dark, pigmented skin on elbows, knuckles, and skinfolds), acne, and androgenic alopecia. Laboratory findings usually include increased luteinizing hormone (LH) levels and LH/follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ratio (> 2), as well as high serum concentration of androgenic hormones, such as testosterone, androstenedione, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree