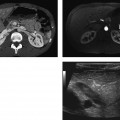
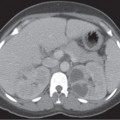
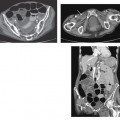
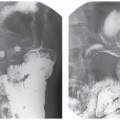
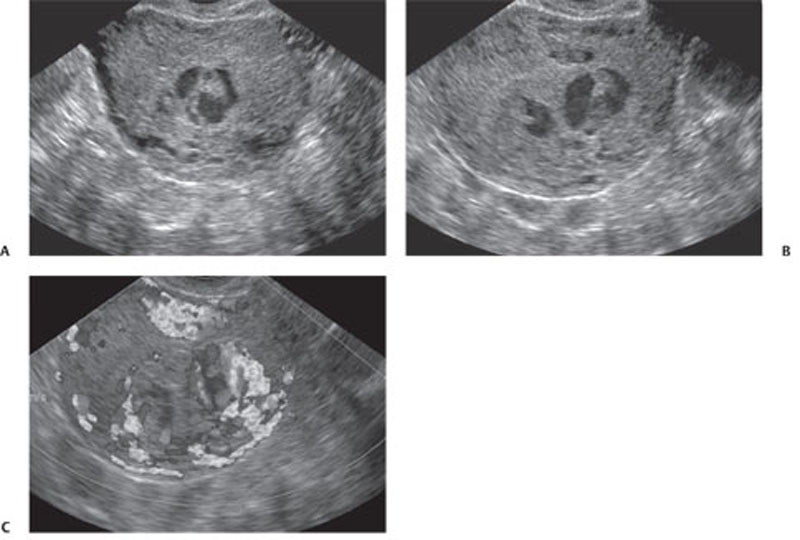
CASE 134 A 27-year-old woman presents with vaginal bleeding. Laboratory test reveal increased levels of β-human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Fig. 134.1 (A–C) Transvaginal ultrasound images show a large intrauterine echogenic solid mass extending through the myometrium and containing multiple hypoechoic cystic spaces. These sonographic features are suggestive of gestational trophoblastic disease. Color Doppler sonography demonstrates increased vascularity within the intrauterine mass, a typical finding in gestational trophoblastic disease. Transvaginal ultrasound images (Fig. 134.1) demonstrate a hypervascular complex intrauterine mass containing many small cysts, extending from the internal os through the fundal endometrium, posterior myometrium, and possibly to or through the posterior serosa. Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) The term gestational trophoblastic disease covers a spectrum of diseases arising from placental trophoblastic tissue after normal or abnormal fertilization. The most common forms of GTD are complete hydatidiform mole (˜80% of cases), invasive mole (chorioadenoma destruens), and choriocarcinoma. Partial hydatidiform moles and placental site trophoblastic tumors are less frequently described. Hydatidiform moles can occur at any age, but they are usually reported in pregnant women in their teens or in their 4th to 5th decades (older patients are more likely to have malignant forms). Several epidemiologic studies have documented broad geographic variations in the prevalence of GTD; higher frequencies have been observed in Asia and Latin America, whereas North America and Europe tend to have a lower incidence. Patients with hydatidiform mole may experience abnormal vaginal bleeding during the first trimester of pregnancy, vaginal discharge of hydropic trophoblastic villi, and severe prolonged hyperemesis gravidarum. Physical examination may reveal a disproportionately enlarged uterus for the estimated gestational age and enlarged ovaries, as well the presence of theca lutein cysts. Increased levels of (β-HCG are associated with all forms of GTD.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree