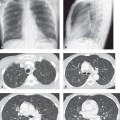
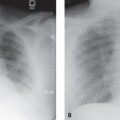
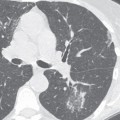
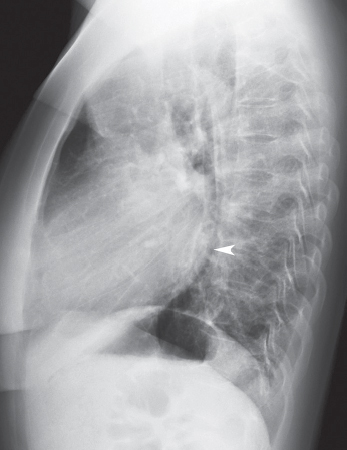
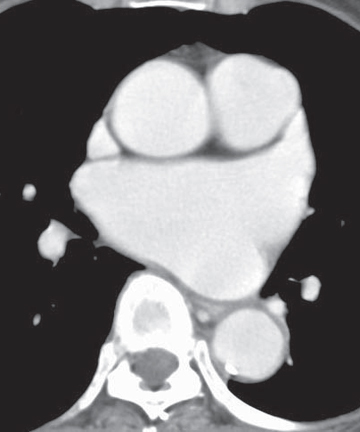
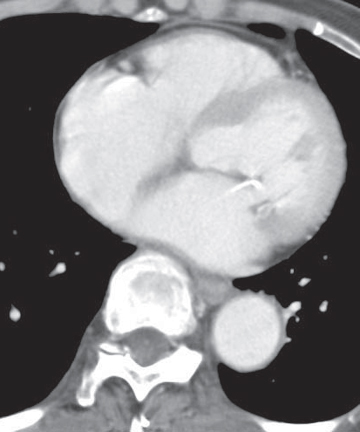
CASE 138 35-year-old woman with dyspnea on exertion PA (Fig. 138.1) and lateral (Fig. 138.2) chest radiographs demonstrate mild cardiomegaly, an enlarged left atrial appendage (arrow) (Fig. 138.1), moderate left atrial enlargement (arrowhead) with elevation of the left mainstem bronchus (Fig. 138.2), and normal pulmonary vascularity. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 138.3, 138.4) shows enlargement of the left atrium and the left atrial appendage (Fig. 138.3). Note calcifications of the mitral valve leaflets (Fig. 138.4). Mitral Stenosis • Left Atrial Enlargement of Other Etiology Fig. 138.1 Fig. 138.2 Fig. 138.3 Fig. 138.4 The mitral valve is characterized by its bicuspid morphology with anterior and posterior leaflets. The anterior mitral valve leaflet is in fibrous continuity with the posterior and left aortic valve leaflets. In normal hemodynamics, diastolic elevation of left atrial pressure forces the mitral valve open and systolic elevation of left ventricular pressure forces it closed. Mitral stenosis refers to valvular obstruction of antegrade blood flow within the left heart and is a lesion of pressure overload. Volume overload follows and results in left atrial enlargement. Rheumatic mitral stenosis almost always has a secondary component of mitral insufficiency.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Myxoma
Myxoma
 Left Atrial Thrombus
Left Atrial Thrombus
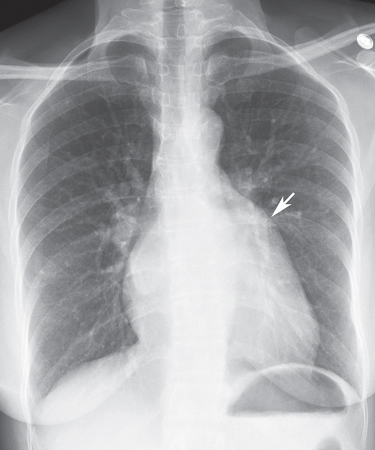
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine