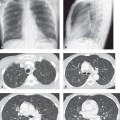
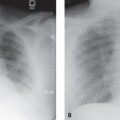
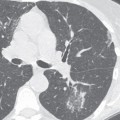
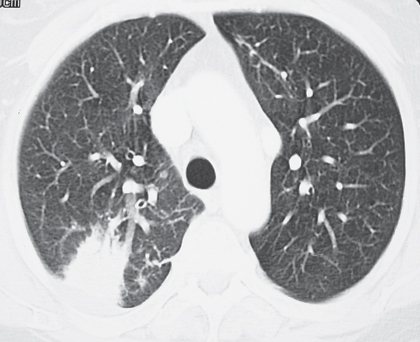
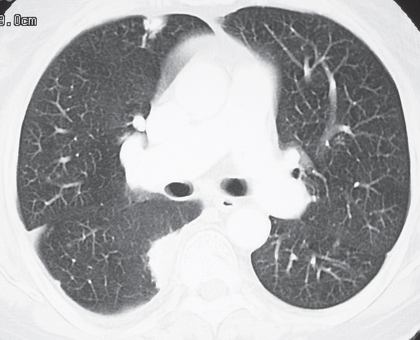
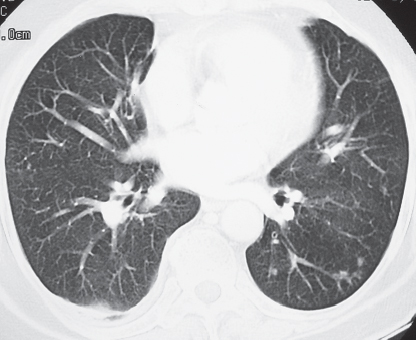
CASE 143 72-year-old woman with cough, sinusitis, and renal insufficiency PA chest radiograph (Fig. 143.1) demonstrates a right upper lobe mass-like consolidation with associated volume loss. Unenhanced chest CT (lung window) (Figs. 143.2, 143.3, 143.4) shows a peripheral wedge-shaped right upper lobe consolidation and multi-focal peripheral subpleural and angiocentric pulmonary masses and nodules. Wegener Granulomatosis or ANCA-Associated Granulomatous Vasculitis • Multicentric Primary or Secondary Neoplasia • Multifocal Pneumonia • Bland or Septic Emboli, Pulmonary Infarcts • Other Pulmonary Vasculitis • Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Fig. 143.1 Fig. 143.2 Fig. 143.3 Fig. 143.4 The pulmonary vasculitides include several disorders characterized by inflammation of the pulmonary blood vessel walls. The term ANCA-associated granulomatous vasculitis has been proposed to replace the eponymous term Wegener granulomatosis, the most common pulmonary vasculitis. The diagnosis of pulmonary vasculitis requires careful correlation of clinical and imaging findings with the underlying histologic features and the exclusion of infectious granulomatous diseases, many of which often exhibit histologic features of vasculitis. The etiology of pulmonary vasculitis is unknown. ANCA-associated granulomatous vasculitis (Wegener granulomatosis) is a systemic necrotizing vasculitis that commonly affects the lung, with an annual incidence of one case per 100,000 population. Although many organs are affected, classical Wegener granulomatosis
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
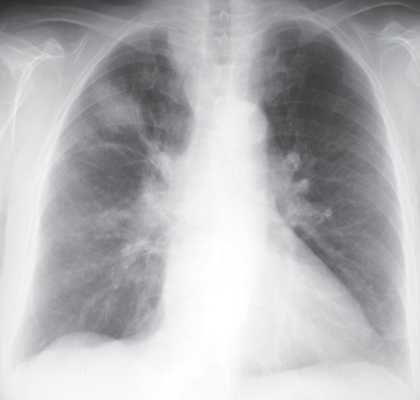
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine