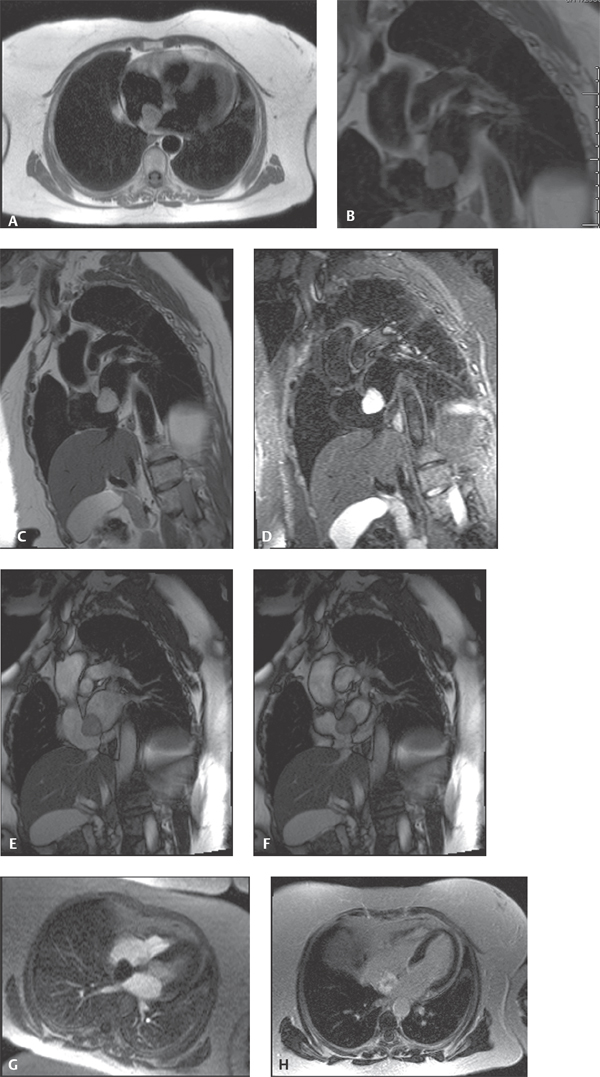
CASE 146 68-year-old woman experiencing dyspnea when lying flat, intermittent palpitations, and chest pain Cardiac MRI: Axial HASTE (Fig. 146.1A) shows a slightly heterogeneous, well-defined right atrial mass adherent to the fossa ovalis slightly higher in signal intensity than normal myocardium. On the T1-weighted short-axis image (Fig. 146.1B) the mass is isointense to muscle, whereas on the T2-weighted short-axis acquisition (Fig. 146.1C) it is much brighter in signal intensity. Short-axis views show that the mass spans the fossa ovalis between the atrial chambers. STIR sequence (Fig. 146.1D) confirms the non-fatty nature of the mass. Short-axis SSFP during diastole (Fig. 146.1E) and systole (Fig. 146.1F) show the mass prolapsing between the atria during the cardiac cycle, which is better appreciated on GRE cine images (not illustrated). Four-chamber perfusion GRE during passage of gadolinium-DTPA (Fig. 146.1G) shows opacification of the atrium but no uptake by the mass itself. Post-Gd-DTPA, four-chamber imaging reveals heterogeneous uptake of contrast by the mass (Fig. 146.1H) Right Atrial Myxoma • Other Primary Cardiac Tumors • Secondary Cardiac Tumors • Atrial Thrombus Secondary cardiac masses are 20–40 times more common than primary cardiac masses. Whereas most secondary cardiac masses are malignant, most primary cardiac masses are benign. Myxoma is the most common primary benign cardiac mass. Approximately 90% of myxomas are solitary pedunculated masses, but as many as 5% may present as multiple masses. These relatively gelatinous tumors most often arise in close proximity to the fossa ovalis. Nearly 75–85% originate in the left atrium, up to 25% occur in the right atrium and/or extend through the fossa ovalis (Figs. 146.1A, 146.1B, 146.1C, 146.1D, 146.1E, 146.1F, 146.1G, 146.1H), and approximately 5% arise within the ventricles. Multiple myxomas may be associated with various syndromes, including Carney syndrome (e.g., atrial myxomas, melanotic schwannomas, Cushing syndrome, multiple cerebral fusiform aneurysms, and breast fibroadenomas). Most cases of atrial myxoma are sporadic. Approximately 10% of myxomas may be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Multiple tumors occur in approximately 50% of familial cases and in these latter cases are more frequently located in the ventricle. Fig. 146.1 (Images courtesy of John D. Grizzard, MD, VCU Medical Center, Richmond, Virginia.) Approximately 75% of sporadic myxomas occur in females. However, the female sexual predilection is less pronounced in familial atrial myxomas. The mean age at presentation for sporadic cases is 56 years, whereas the mean age for familial myxoma is 25 years. Most patients with sporadic myxomas
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine