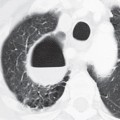
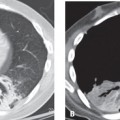
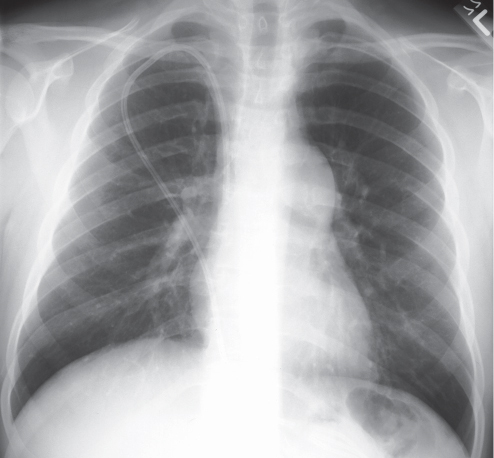
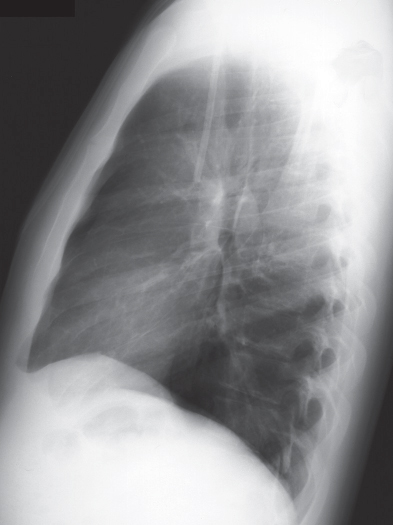
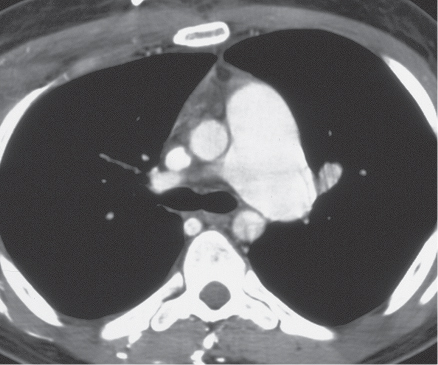
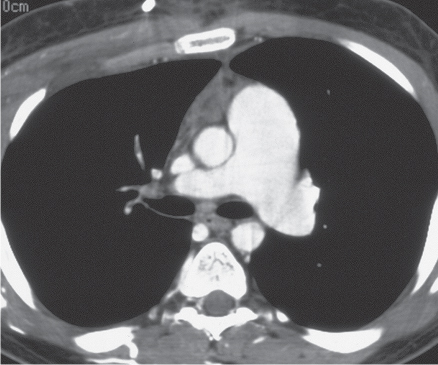
CASE 15 22-year-old man evaluated for newly diagnosed leukemia PA (Fig. 15.1) and lateral (Fig. 15.2) chest radiographs demonstrate enlargement of the main pulmonary artery. The heart and peripheral pulmonary vasculature are normal. Note the central venous catheter with its tip in the superior vena cava. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 15.3, 15.4) demonstrates marked enlargement of the pulmonary trunk and the left pulmonary artery with a normal right pulmonary artery (Fig. 15.4) Pulmonic Stenosis • Patent Ductus Arteriosus • Pulmonary Artery Hypertension Fig. 15.1 Fig. 15.2 Fig. 15.3 Fig. 15.4 (Images courtesy of Diane C. Strollo, MD, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.) Pulmonic stenosis is the most common anomaly that produces obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract. It occurs as an isolated anomaly in up to 7% of patients with congenital heart disease. It is a common congenital cardiac lesion among those that initially manifest in adulthood. Pulmonic stenosis may be associated with other congenital heart lesions and is a component of tetralogy of Fallot.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine