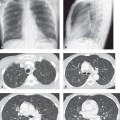
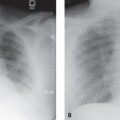
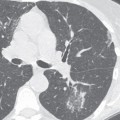
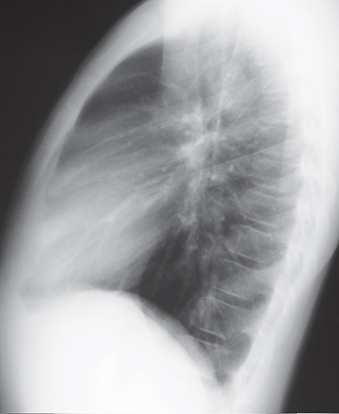
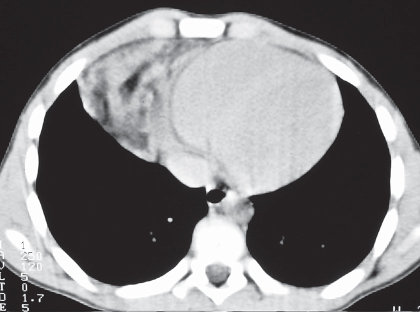
CASE 155 Asymptomatic 12-year-old boy PA (Fig. 155.1) and lateral (Fig. 155.2) chest radiographs demonstrate a right anterior-inferior mediastinal mass that conforms to the shape of the heart and mimics cardiomegaly. Note the lesion is not visible on the lateral chest radiograph (Fig. 155.2). Unenhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Fig. 155.3) shows a well-defined right juxtacardiac mass composed of soft-tissue elements intermixed with areas of fat. Note mild mass effect on the heart and visualization of intact adjacent subepicardial fat. Thymolipoma • Morgagni Hernia • Lipoma/Liposarcoma • Mature Teratoma Fig. 155.1 Fig. 155.2 Fig. 155.3 Fig. 155.4 Unenhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) of an obese 40-year-old man with mediastinal lipomatosis demonstrates fat attenuation tissue surrounding normal mediastinal structures without resultant mass effect. Thymolipoma is a rare benign primary thymic neoplasm. Thymolipomas are characterized by their soft consistency and preferential growth in the inferior portion of the anterior mediastinum. These lesions may reach very large sizes in spite of minimal symptoms. The etiology of thymolipoma is unknown. Patients with thymolipoma are usually young adults in the third decade of life, and men and women are equally affected. Patients may be entirely asymptomatic. Symptomatic patients present with complaints related to mass effect by large lesions and may complain of cough, dyspnea, and/or chest pain.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Imaging Features
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine