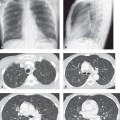
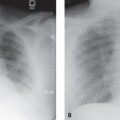
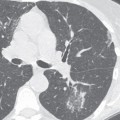
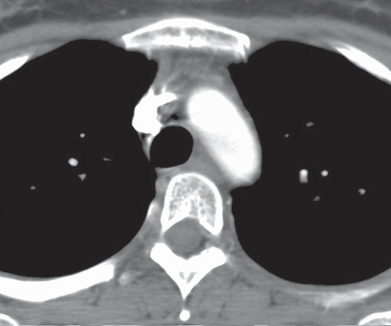
CASE 156 Asymptomatic 42-year-old woman status post chemotherapy for malignancy Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Fig. 156.1) demonstrates diffuse enlargement of a homogeneous thymus without mass effect, local invasion, or lymphadenopathy. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Fig. 156.2) performed after corticosteroid therapy demonstrates prompt reduction in the size of the thymus and a normal anterior mediastinum. Thymic Hyperplasia • Thymoma • Lymphoma Thymic hyperplasia is an uncommon condition that results in a global increase in the size and weight of the thymus (based on the expected size of the thymus for the individual’s age). The condition is also known as “true” thymic hyperplasia and as “rebound” thymic hyperplasia; the latter term is used specifically when hyperplasia follows chemotherapy, steroid therapy, or recovery from a severe systemic insult. Rebound thymic hyperplasia is typically defined as a 50% increase in thymic volume over baseline. Fig. 156.1 Fig. 156.2
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
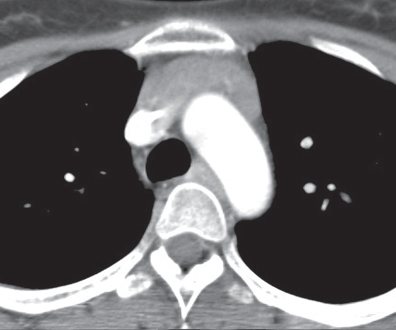
Etiology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree