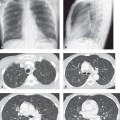
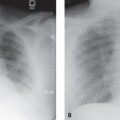
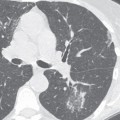
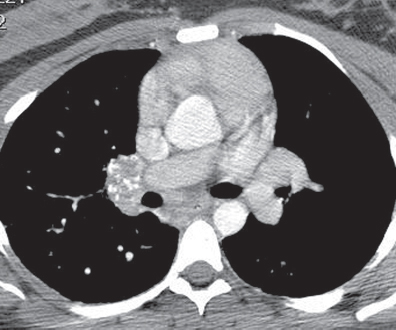
CASE 160 28-year-old woman with chest pain and dyspnea PA chest radiograph (Fig. 160.1) demonstrates decreased right lung volume, right hilar fullness, and paucity of right lower lobe vasculature. Axial and coronal contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 160.2, 160.3) shows a right hilar soft-tissue mass with multifocal internal calcifications that obliterates the lumen of the right pulmonary artery. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (lung window) (Fig. 160.4) reveals attenuation in the caliber of the right lower lobe pulmonary arteries and right lower lobe peripheral ground glass opacity. Mediastinal Fibrosis • Lung Cancer • Lymphoma • Metastatic Mediastinal Lymphadenopathy • Other Non-Neoplastic Lymphadenopathies Fig. 160.1 Fig. 160.2 Mediastinal fibrosis is the proliferation of dense fibrous tissue in the mediastinum with resultant focal or infiltrative masses, which may be locally invasive.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Mycobacterial Infection
Mycobacterial Infection
 Fungal Disease
Fungal Disease
 Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
 Silicosis
Silicosis
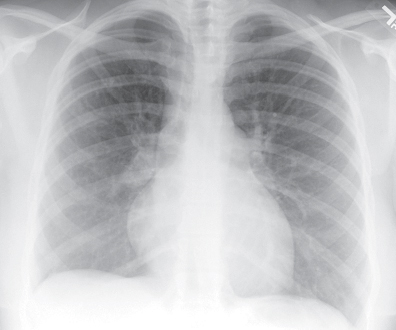
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree