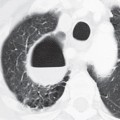
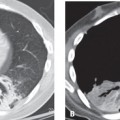
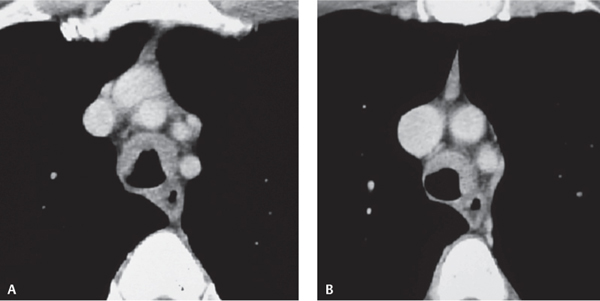
CASE 22 56-year-old woman with cough Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 22.1A, 22.1B) demonstrates abnormal soft tissue extending anterolaterally along the tracheal wall and narrowing the lumen. Note the absence of soft-tissue infiltration/obliteration of peritracheal tissue planes. Tracheobronchial Amyloidosis • Primary and Secondary Neoplasia (e.g., adenoid cystic carcinoma, tracheal metastases) • Wegener Granulomatosis • Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica Fig. 22.1 Amyloidosis is a rare disease that may affect the lung or tracheobronchial tree. It may occur as a primary lesion or as secondary amyloid deposition in association with chronic disease. Tracheobronchial involvement is the most common and severe form of thoracic amyloidosis. Primary tracheal amyloidosis is rare and usually involves the trachea in a slow and indolent manner. The etiology of tracheobronchial amyloidosis is unknown. Chronic diseases associated with secondary amyloidosis include rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn disease, ankylosing spondylitis, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, and familial Mediterranean fever.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree