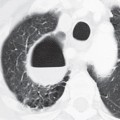
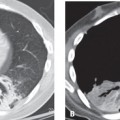
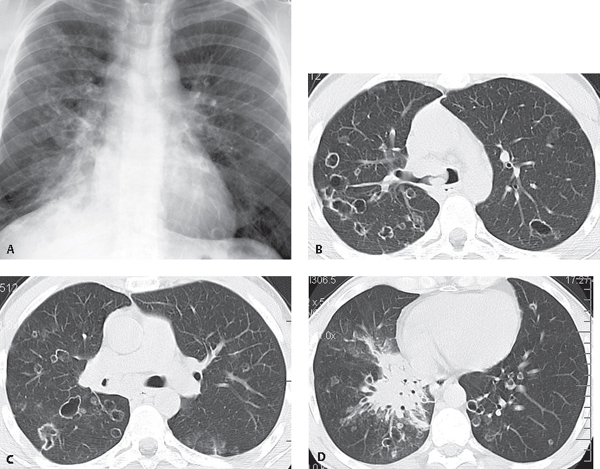
CASE 23 27-year-old man with fever and malaise and known tracheobronchial papillomatosis PA chest radiograph (Fig. 23.1A) demonstrates right lower lobe consolidation and bilateral irregular cystic lung lesions more numerous in the right lung. Unenhanced chest CT (lung window) (Figs. 23.1B, 23.1C, 23.1D) demonstrates multifocal thin-walled cystic lung lesions with variable shapes and endobronchial soft-tissue masses affecting the carina, right mainstem bronchus, and bronchus intermedius (Figs. 23.1B, 23.1C). Note also the near complete obstruction and circumferential thickening of the bronchus intermedius by an endobronchial papilloma (Fig. 23.1C) and right lower lobe consolidation and infrahilar mass (Fig. 23.1D). At endoscopy, squamous cell carcinoma was diagnosed. Fig. 23.1 Tracheobronchial Papillomatosis; Complicating Squamous Cell Carcinoma • Pulmonary Metastases • Multifocal Cavitary Primary Lung Cancer • Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis • Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia • Vasculitis Papillomas are the most common laryngeal tumor of young children. Tracheobronchial papillomatosis is a pre-malignant condition that results from tracheobronchial dissemination of laryngeal papillomas. It is also known as recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. The lesions typically involve the larynx but extend into the trachea and proximal bronchi in 5% of cases and into the small airways and lung parenchyma in less than 1%.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree