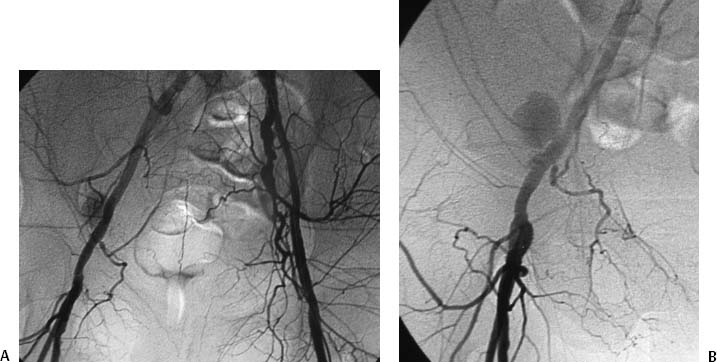
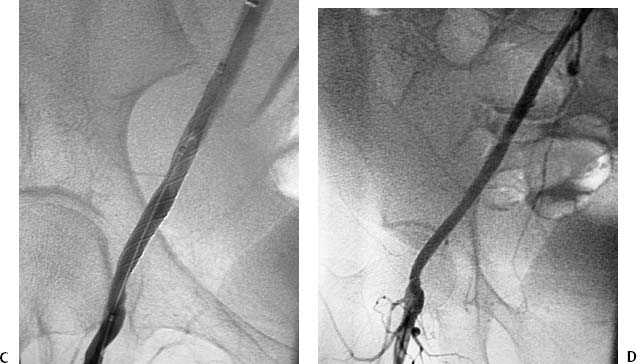
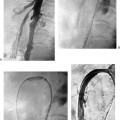
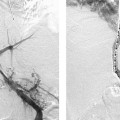
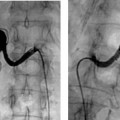
CASE 26 A 43-year-old male sustained a stab wound to his right pelvis. Physical exam revealed a bruising and pulsatile mass in the right inguinal region with a palpable thrill. The patient was placed on antibiotics, and an arteriogram was performed to evaluate the possibility of vascular injury. Figure 26-1 Stent graft repair of traumatic pseudoaneurysm. (A) Pelvic arteriogram shows saccular aneurysm of the distal right external iliac artery. (B) Selective right common iliac arteriogram shows pseudoaneurysm. (C) Selective right iliac arteriogram obtained immediately after stent graft deployment shows exclusion of aneurysm. (D) Final right iliac arteriogram shows widely patent graft and no evidence of aneurysm filling. The right common femoral artery was catheterized using the Seldinger technique and a Balkan sheath was placed. A pigtail catheter was advanced into the abdominal aorta and pelvic arteriography was performed, which revealed a saccular outpouching from the right external iliac artery (Fig. 26-1A). Right external iliac artery pseudoaneurysm. Puncture needle Vascular sheath 5F pigtail and endhole catheters 0.035″ conventional and hydrophilic soft-tipped guidewires Contrast material Conventional angioplasty balloons Inflation syringe Covered stents Due to the size and location of the pseudoaneurysm and the likelihood of a large rent from the stab wound, stent graft insertion was deemed a better therapeutic option than thrombin injection. The contralateral common femoral artery was then catheterized over the aortic bifurcation using the pigtail catheter. Selective arteriography defined the position of the aneurysm (Fig. 26-1B). The catheter and guidewire combination was advanced distally to the common femoral artery. The sheath was then advanced over the bifurcation and positioned above the aneurysm. The pigtail catheter was then exchanged for an 8-mm × 4-cm long covered stent, which was deployed across the aneurysm. Follow-up arteriography showed no residual filling with rapid antegrade flow to the foot (Figs. 26-1C, D).
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Studies
Angiogram
Diagnosis
Treatment
Equipment
Stent Graft Repair
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree