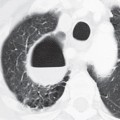
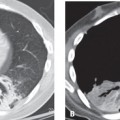
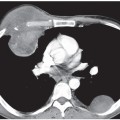
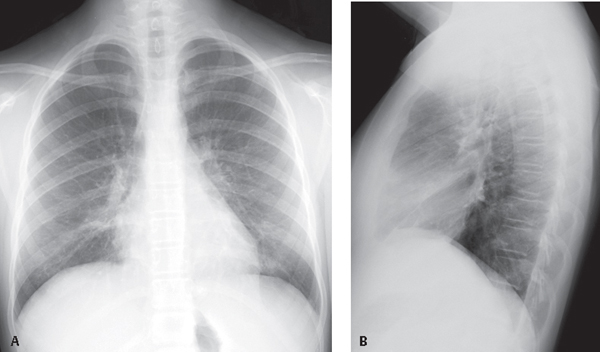
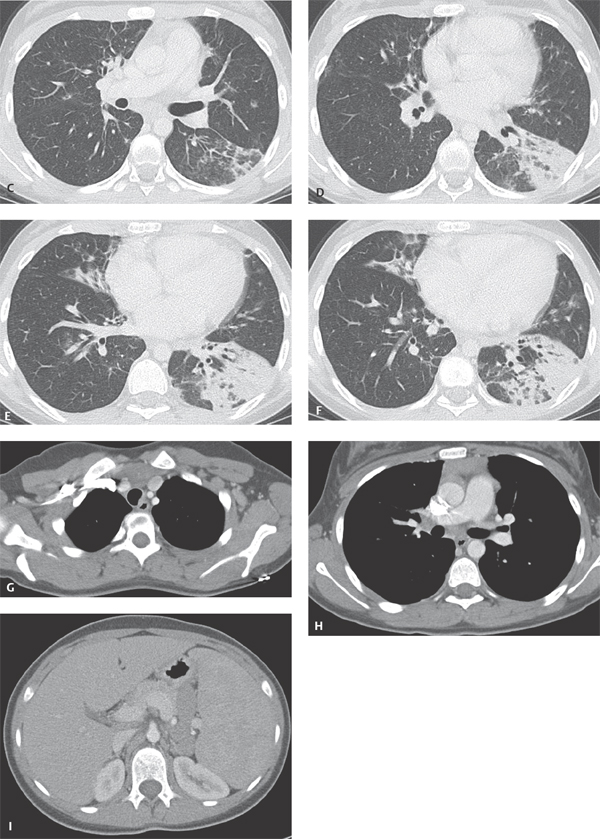
CASE 32 Young adult woman presenting with the fourth episode of recurrent pneumonia over the past 18 months PA (Fig. 32.1A) and lateral (Fig. 32.1B) chest radiographs demonstrate central perihilar bronchial wall thickening and air space disease in the retrocardiac region left lower lobe and right middle lobe, the latter associated with some volume loss. Chest CT (Figs. 32.1C, 32.1D, 32.1E, 32.1F) (lung window) shows left lower lobe consolidation, bronchial dilatation, and bronchiectasis. Similar changes are seen to a lesser degree in the right middle lobe, with associated volume loss. There are areas of scarring in the right middle and lower lobe, scattered air space, and centrilobular nodules. Bronchiectatic airways parallel the right inferior pulmonary vein (Fig. 32.1E). Contrast-enhanced chest CT (Figs. 32.1G, 32.1H, 32.1I) (mediastinal window) reveals anterior mediastinal and left subpectoral lymphadenopathy (Fig. 32.1G), right hilar and subcarinal lymphadenopathy (Fig. 32.1H), and subdiaphragmatic lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly (Fig. 32.1I). Residual thymus tissue is seen (Fig. 32.1H). Common Variable Immune Deficiency Syndrome with Community-Acquired Pneumonia • Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Syndrome • Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia Secondary to Infection • X-linked Agammaglobulinemia (XLA) Fig. 32.1 Common variable immune deficiency syndrome (CVID), also called hypo-gammaglobulinemia or adult-onset hypo-gammaglobulinemia, is a relatively common primary immune deficiency. CVID is characterized by low levels of most or all immunoglobulins, lack of B-lymphocytes or plasma cells capable of producing antibodies, and recurrent bacterial infections. Both humoral and cell-mediated lymphocytic responses are affected. The etiology of CVID is unknown. Most patients present sporadically, although up to 20% of patients have a first-degree relative with selective IgA deficiency. CVID is also reportedly associated with the use of various antirheumatic (e.g., sulfasalazine) or antiepileptic (e.g., hydantoin, carbamazepine) drugs.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine