Case 59
Indication: Screening.
History: Unremarkable.
Risk profile: No increased risk.
Age: 43 years.
Clinical Findings
Mobile resistance in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast.
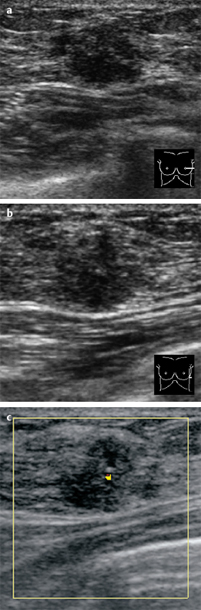
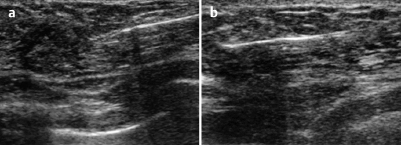
Fig. 59.1 a-c Conventional and color-coded Doppler sonography.
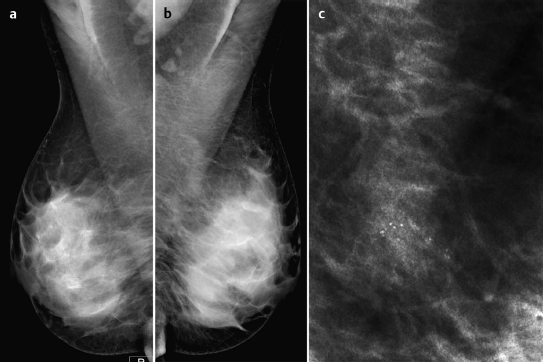
Fig. 59.2a–c Digital mammography (MLO) with magnification view of the left breast.
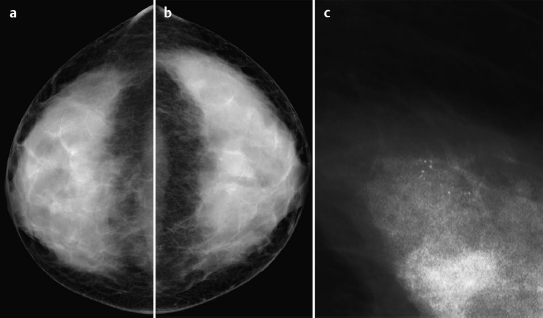
Fig. 59.3a–c Digital mammography (CC) with magnification view of the left breast.
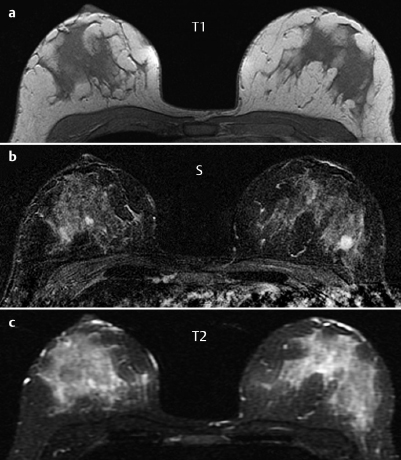
Fig. 59.4a–c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts.
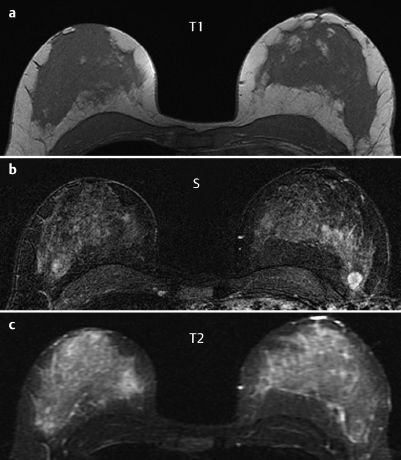
Fig. 59.5a–c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts.
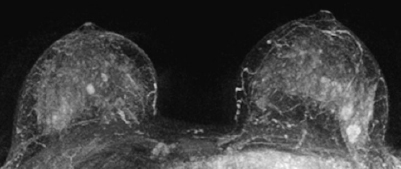
Fig. 59.6 Contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Maximum intensity projection.

|
Please characterize ultrasound, mammography, and MRI findings.
What is your preliminary diagnosis?
What are your next steps? |
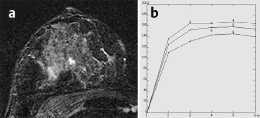
Fig. 59.7a,b Signal-to-time curves.
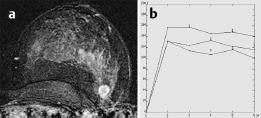
Fig. 59.8a,b Signal-to-time curves.
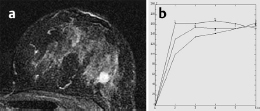
Fig. 59.9a,b Signal-to-time curves
The imaging of a woman presenting for screening is shown. The palpable resistance was first detected in the clinical examination.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound demonstrated a lobulated, inhomogeneously hypoechoic lesion, 12 mm in diameter, without distal shadowing in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. There was no evident architectural distortion. In the central part of the left breast, Doppler sonography showed signs of arterial hyperperfusion. US BI-RADS left 4.
Mammography
There was symmetric extremely dense glandular tissue, ACR type 4, visible in mammography. No masses or densities could be identified. However, there was a cluster of predominantly monomorphous microcalcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. BI-RADS right 1/left 4. PGMI: CC view P; MLO view P.
MR Mammography
MRI showed a diffuse, variegated contrast uptake throughout the parenchyma. In the upper outer quadrant of the left breast, a lesion of 13 mm diameter with ring enhancement, initial signal increase of 190%, and postinitial washout was visible. This lesion showed intermediate signal in T2-weighted imaging. There was another ill-defined lesion with inhomogeneous enhancement, initial signal increase of 160%, and postinitial plateau nearby. In the central parts of the right breast a lobulated septate lesion with a high water component in inversion recovery sequence was seen.
MRI Artifact Category: 1
MRI Density Type: 2
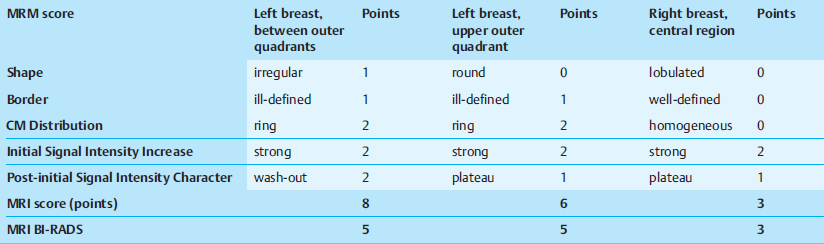
 Preliminary Diagnosis
Preliminary Diagnosis
Left: Bifocal carcinoma.
Right: Fibroadenoma, adenosis, carcinoma.

















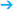 Preliminary Diagnosis
Preliminary Diagnosis