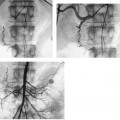
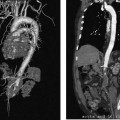
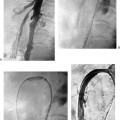
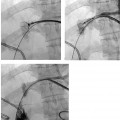
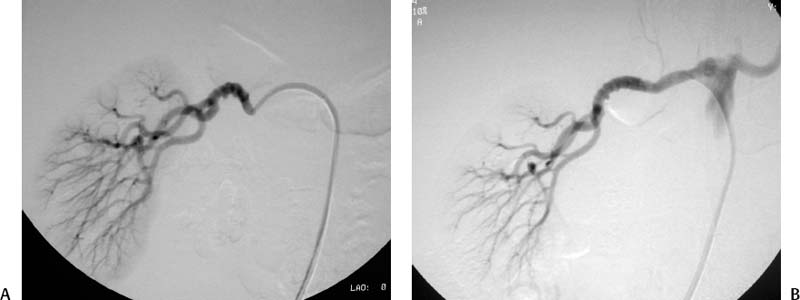
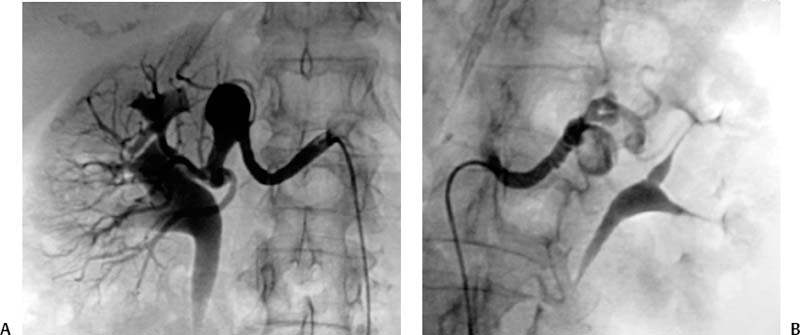
CASE 59 A 45-year-old male was referred to the radiology department after negative work-up for medical causes of hypertension. Physical exam revealed a blood pressure of 174/105 mm Hg. Figure 59-1 A 45-year-old male presented with hypertension. (A) Selected right renal angiogram shows a “beaded” appearance resulting from multiple stenoses of the right main renal artery, sparing the medial third. (B) Follow-up selected angiography after angioplasty to 6 mm in diameter shows marked improvement in luminal diameter though the beaded appearance persists. Persistence of the angiographic appearance is common in the immediate follow-up period, but often improves over time. Sonographic examination of the right kidney revealed normal parenchymal echogenicity and size. Doppler interrogation revealed elevated resistive index. Renal angiography revealed multiple focal stenosis of the main right renal artery with a “beaded” appearance, sparing the medial third (Fig. 59–1A). Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) of the renal artery. The right common femoral artery was accessed using a Micropuncture set (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) and a 6-French (F) Balkan sheath (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) was advanced over a standard 0.035-inch guidewire. Five thousand U of intravenous heparin were administered. Through the sheath, a 5F visceral selective catheter (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) was used to select the right renal artery and angiography was performed (finding described above). A 0.035-inch Magic Torque wire (Cordis) was used to cross the stenotic segment, and dilatation was performed using an Ultrathin balloon catheter (Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts) with a diameter of 6 mm and a length of 2 cm. Follow-up selected angiography performed through the sheath showed marked improvement (Fig. 59-1B). Two days after the procedure, the blood pressure had decreased to 140/80, remaining near this level during a 1-year follow-up period. The patient required no antihypertensive medication. Figure 59-2 A 40-year-old female presented with hypertension and flank pain. (A) Selected right renal artery angiogram shows a true aneurysm involving the main right renal artery. (B) Selected left renal artery angiogram shows a beaded appearance indicating fibromuscular dysplasia, in addition to a true aneurysm. Micropuncture set (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) 6F Balkan sheath (Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) Standard J wire (Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts) 5F visceral selective catheter (RC1; Cook, Bloomington, Indiana) 0.035” Magic Torque wire Ultrathin balloon catheter (6 × 20 mm; Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts)
Clinical Presentaton
Radiologic Studies
Diagnosis
Treatment
Equipment
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree