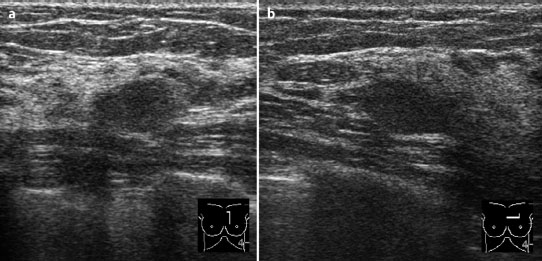
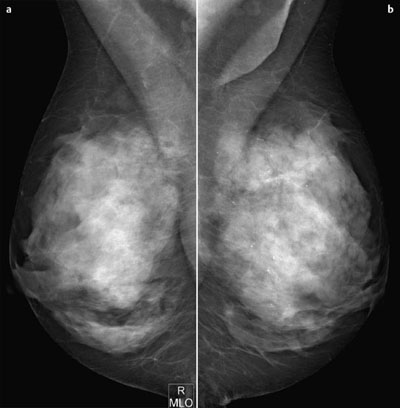
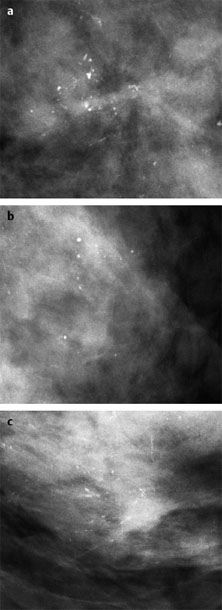
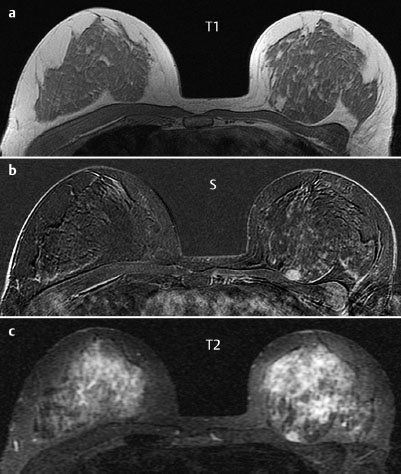
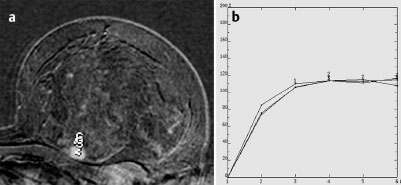
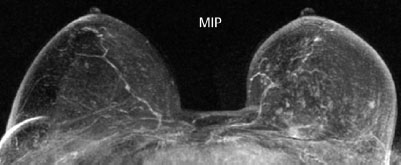
Case 6 Indication: Screening. History: Unremarkable. Risk profile: Breast cancer of mother (premenopausal) and sister (perimenopausal). Age: 59 years. Fig. 6.1 a,b Sonography. Normal. Fig. 6.2a,b Digital mammography, MLO view. Fig. 6.3a–c Magnification view of the left breast cranial (a), central (b) and caudal (c). Fig. 6.4a–c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. Fig. 6.5a,b Signal-to-time curves. Fig. 6.6 Contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Maximum intensity projection. Please characterize ultrasound, mammography, and MRI findings. What is your preliminary diagnosis? What are your next steps? This asymptomatic woman underwent screening imaging because of her increased familial risk. Round lesion with smooth borders in the upper inner quadrant of the left breast close to the pectoral muscle. Homogeneous internal echo pattern. Long axis parallel to skin. Slight distal acoustic enhancement. No definitive criteria of malignancy. US BI-RADS 3. Bilaterally symmetric extremely dense parenchymal pattern, ACR type 4. Within the limitations of these conditions, no mass was detected. No architectural distortion. Diffuse microcalcifications in the left breast, with varying characteristics:
Clinical Findings

Ultrasound
Mammography
Cranial: | regionally polymorphous (BI-RADS 4) |
Central: | regionally monomorphous (round) (BI-RADS 2) |
Caudal: | segmentally polymorphous (BI-RADS 5) |
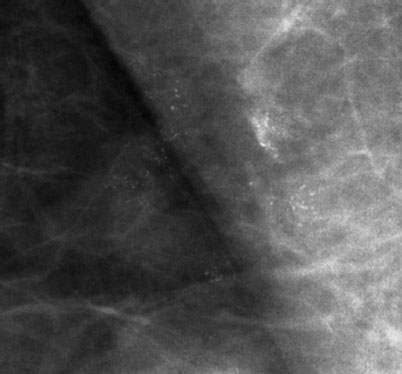
Did you note the microcalcifications in the axillary region of the right breast (Fig. 6.7)? How do you interpret these?
Categorization of mammography findings: BI-RADS right 3/left 5. PGMI: MLO view P (despite axillary fold visible left).
MR Mammography
There is a round hypervascularized lesion 1 cm in diameter in the upper inner quadrant of the left breast, obviously corresponding to the lesion seen in ultrasound. This lesion has high signal intensity (water content) in the inversion recovery sequence and a nonspecific signal-time curve with maximum 110% initial increase and subsequent plateau.
Fig. 6.7 Mammography, magnification view of the upper outer quadrant of the right breast.
MRI Artifact Category: 2
MRI Density Type: 1
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Left breast, upper inner quadrant: | Fibroadenoma, papilloma, phyllodes tumor, carcinoma (mucinous, medullary?) |
Left breast, cranial and caudal regions: Left breast, central region: Right axillary region: | DCIS, IDC adenosis, DCIS adenosis, DCIS |
MRM score | Finding | Points |
Shape | round | 0 |
Border | well-defined | 0 |
CM Distribution | homogeneous | 0 |
Initial Signal Intensity Increase | strong | 2 |
Post-initial Signal Intensity Character | plateau | 1 |
MRI score (points) |
| 3 |
MRI BI-RADS |
| 3 |
BI-RADS Categorization | ||
Clinical Findings | right 1 | left 1 |
Ultrasound | right 1 | left 3 |
Mammography | right 3 | left 5 |
MR Mammography | right 1 | left 3 |
BI-RADS Total | right 3 | left 5 |
Procedure
MR-guided vacuum core biopsy of the lesion in the left breast close to the chest wall. Alternatively, US-guided core biopsy, it being likely although not certain that this lesion corresponds with the US findings. Stereotactic vacuum core biopsy of the cranially or caudally located microcalcifications. Excisional biopsy for diagnostic purposes of the calcifications of the right axillary region after preoperative marking.
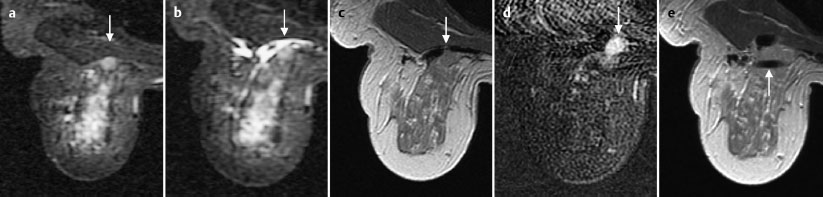
Fig. 6.8a–e MR-guided vacuum biopsy of the hypervascularized lesion in the left breast. Documentation of the lesion (arrow) in water-sensitive IR-sequence before (a) and after local anaesthesia (b). T1-weighted image (c), subtraction image (d) and documentation of the positioned coaxial canula (arrow) after removal of specimen (e).
Histology of the lesion close to the chest wall, left breast
Mucinous carcinoma.
Histology of the microcalcifications, left breast cranial region:
Intraductal carcinoma.
Histology
Left breast: Invasive mucinous carcinoma pT1c (11 mm)+extensive DCIS pNO (0/14 sn), G3 (DCIS)
Right breast: Adenofibrous dysplasia. No malignancy.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree