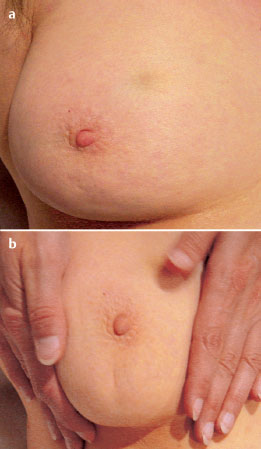
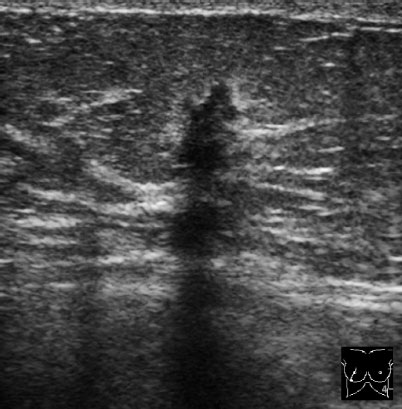
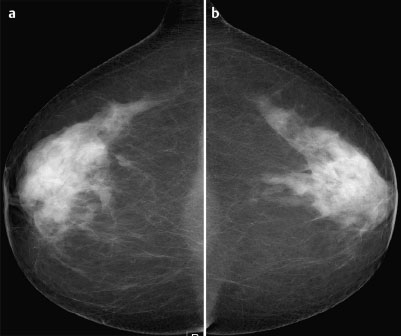
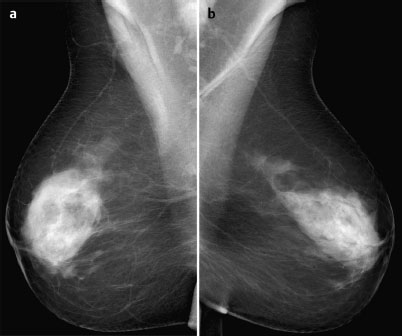
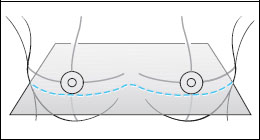
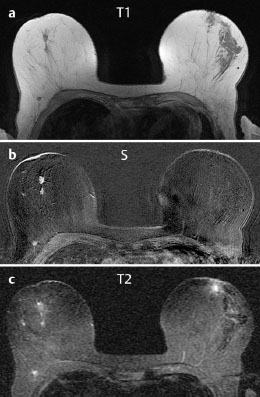
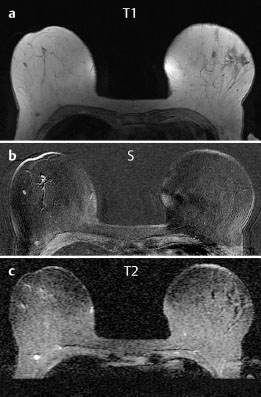
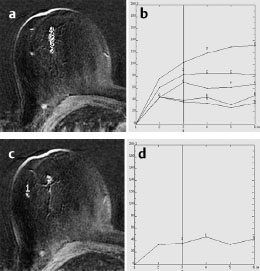
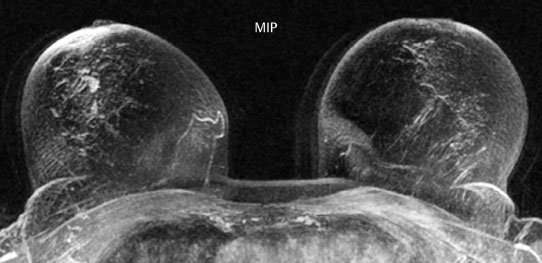
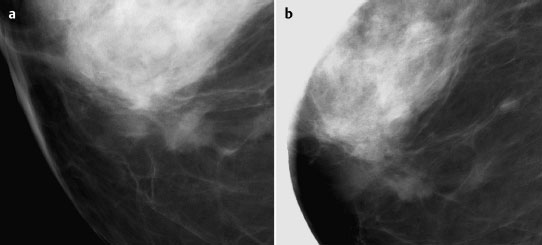
Case 8 Indication: Screening. History: Unremarkable. Risk profile: No increased risk. Age: 68 vears. Fig. 8.1 a,b Clinical examination of the right breast. No palpable mass. Fig. 8.2 Sonography. Fig. 8.3a,b Digital mammography, CC view. Fig. 8.4a,b Digital mammography, MLO view. Fig. 8.5a–c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. Fig. 8.6a-c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. Fig. 8.7a-d Signal-to-time curves. Fig. 8.8 Contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Maximum intensity projection. Please characterize ultrasound, mammography, and MRI findings. What is your preliminary diagnosis? What are your next steps? Clinical symptoms were present and imaging was performed for screening purposes. With the patient’s arms raised, and on compression of the right breast with both hands, there was a suspicious skin retraction below the nipple. Ultrasound demonstrated a suspect 6 mm-long mass with a hyperechoic margin. The long axis of this lesion was perpendicular to the skin, disrupting the continuity of the surrounding ligaments. US BI-RADS right 5. The parenchyma in both breasts was dense, ACR type 4, and bilaterally symmetric. No calcifications. The MLO view of the right breast showed a lobulated density of approx. 8 mm diameter caudal of the glandular tissue However, this finding was obscured by the parenchyma in the CC view (BI-RADS right 3/left 1). For better differentiation, spot compression of the unclear density in the right breast was performed (Fig. 8.9b). This view depicted the spiculated periphery of this lesion (BI-RADS including spot view: right 4). PGMI: CC view P; MLO view G (caudal inframammary fold). Corresponding to ultrasound and mammography findings, MRI showed a hypervascularized lesion in the right breast inferior to the nipple. A second small lesion with increased vascularization was visible toward the chest wall. A third lesion was seen lateral to the primary tumor. Hypervascularized lymph nodes. MRI Artifact Category: 2 MRI Density Type: 1 Fig. 8.9a,b Magnification of the MLO view (right breast) and additional spot compression.

Clinical Examination
Ultrasound
Mammography
MR Mammography
MRM score | Finding | Points |
Shape | oval | 0 |
Border | spiculated | 1 |
CM Distribution | inhomogeneous | 1 |
Initial Signal Intensity Increase | moderate | 1 |
Post-initial Signal Intensity Character | plateau | 1 |
MRI score (points) |
| 4 |
MRI BI-RADS |
| 4 |
 Preliminary Diagnosis
Preliminary Diagnosis
Multifocal breast cancer. No differential diagnoses.
BI-RADS Categorization | ||
Clinical Findings | right 4 | left 1 |
Ultrasound | right 5 | left 1 |
Mammography | right 3 (4 after spot) | left 1 |
MR Mammography | right 4 (multifocal) | left 1 |
BI-RADS Total | right 4 | left 1 |
Procedure
Histological verification of the primary tumor of the right breast by percutaneous US-guided core biopsy.
Histopathology of the right breast after US-guided core biopsy
Invasive ductal carcinoma.
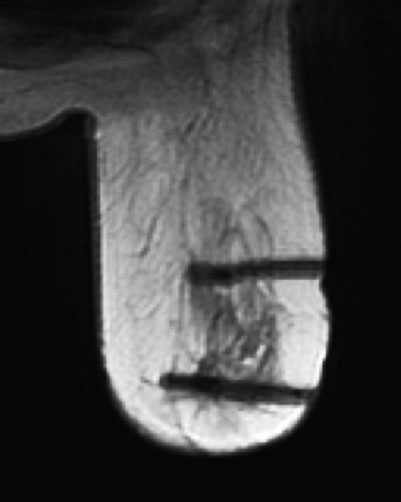
Preoperative MR-guided localization of the multifocal nodules peripheral to the primary tumor (Fig. 8.10).
Fig. 8.10 Preoperative MR-guided localization with two hook-wires.
Diagnosis
Bifocal invasive ductal carcinoma of the right breast (13 mm, 7 mm).
IDC pT1 c (bifocal), pN1 (1/5 sn), G2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree