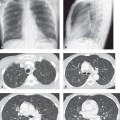
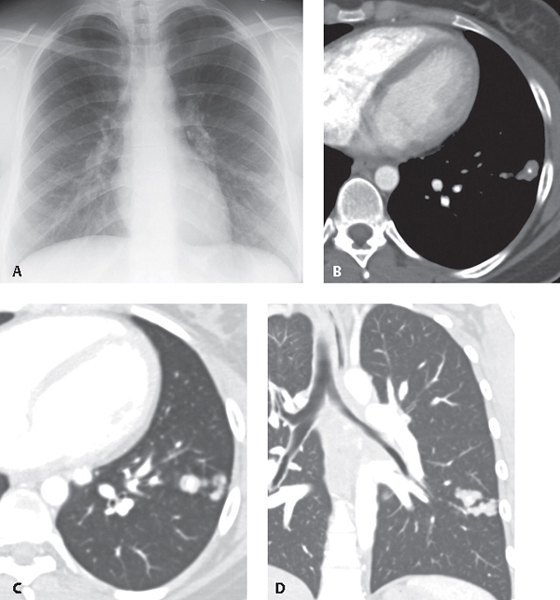
CASE 61 Asymptomatic 30-year-old woman evaluated for an enlarging lung lesion PA chest radiograph (Fig. 61.1A) demonstrates a multi-lobulated left lower lobe nodule and ipsilateral calcified hilar lymph nodes. Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal and lung windows) (Figs. 61.1B, 61.1C, 61.1D) demonstrates clustered non-enhancing left lower lobe nodules with intrinsic round calcifications. The clustered nature of the lesions is best visualized on the coronal reformatted CT image (Fig. 61.1D). Histoplasmosis Fig. 61.1 • Granulomas; Other Fungal Infections • Granulomas; Tuberculosis Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection endemic to the south-central United States, especially the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys. Histoplasmosis is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus transmitted through inhalation of airborne spores typically released from infected soil enriched by bird droppings or guano. Inhaled organisms multiply within macrophages and undergo lymphatic and hematogenous dissemination. Cellular immunity develops within two weeks, with subsequent healing.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree