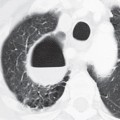
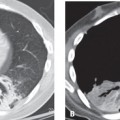
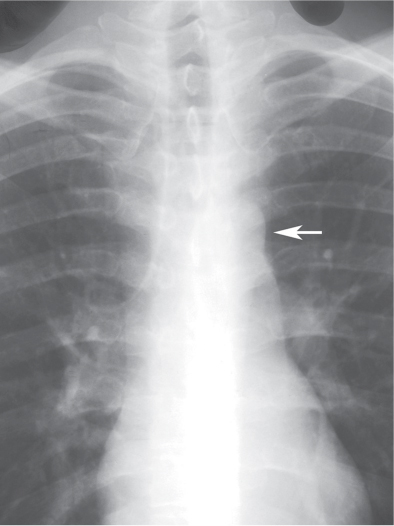
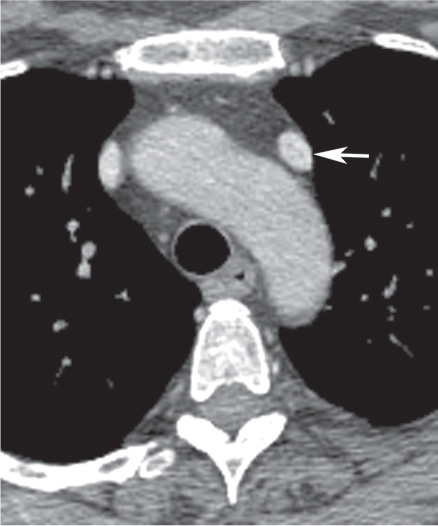
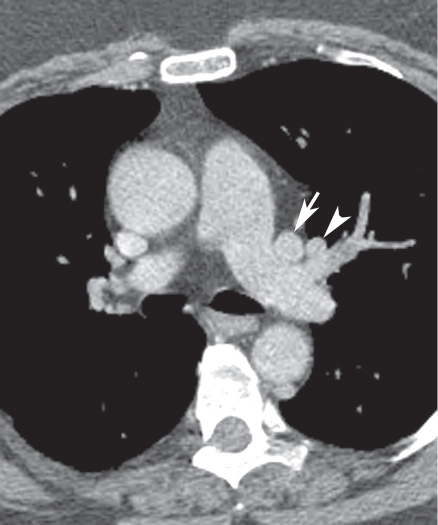
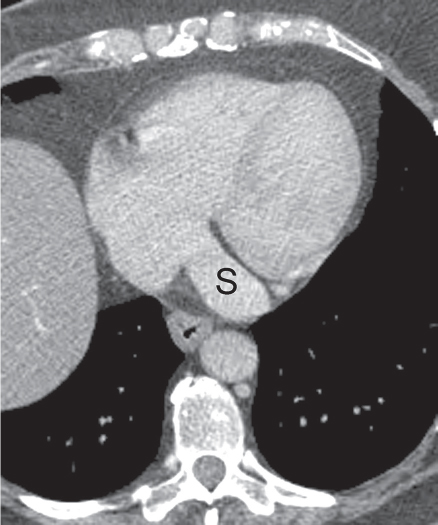
CASE 8 Asymptomatic 30-year-old man Coned-down PA chest radiograph (Fig. 8.1) demonstrates a subtle vertically oriented left paramediastinal interface lateral to the aortic arch (arrow). Contrast-enhanced chest CT (mediastinal window) (Figs. 8.2, 8.3, 8.4) demonstrates a persistent left superior vena cava (arrow) coursing vertically along the left superior mediastinum lateral to the aortic arch (Fig. 8.2). The vessel courses medial to the left superior pulmonary vein (arrowhead) (Fig. 8.3) and drains into a dilated coronary sinus (S) (Fig. 8.4). Note the coexistent small-caliber right superior vena cava (Figs. 8.2, 8.3) Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava Left Upper Lobe Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (PAPVR) Fig. 8.1 Fig. 8.2 (Images courtesy of Maysiang Lesar, MD, National Naval Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.) Fig. 8.3 Fig. 8.4 A persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is a relatively common anomaly and represents the most frequent form of anomalous venous return to the heart. It occurs in approximately 0.3–0.5% of the general population, with an increased prevalence (4.4%) in patients with congenital heart disease.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine