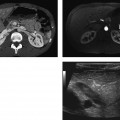
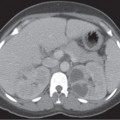
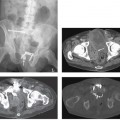
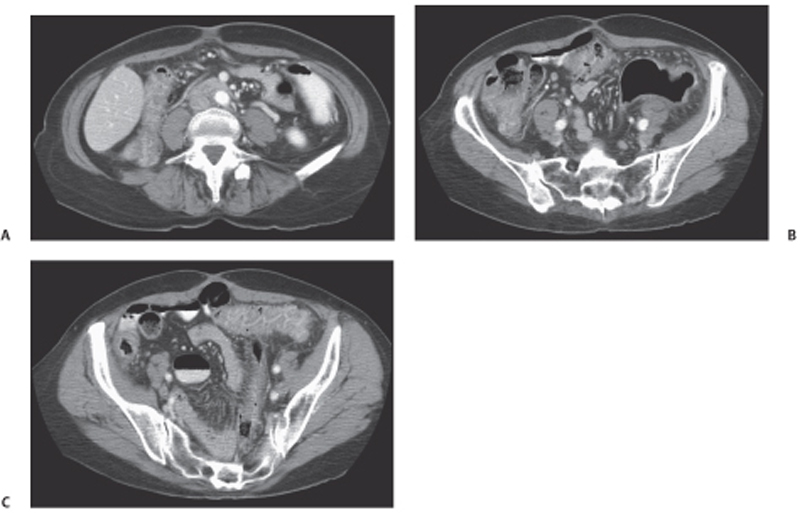
CASE 85 A 42-year-old man presents with abdominal cramps, fever, and diarrhea. Fig. 85.1 (A) An axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows severe bowel wall thickening and enhancement of the ascending colon. (B) Inferior axial scan shows prominent lymph nodes scattered in the mesenteric fat, likely reactive. This finding may favor the infectious etiology of colitis. (C) Axial image through the pelvis shows involvement of the distal large bowel with prominent mesocolic vasculature. Axial computed tomography (CT) images (Fig. 85.1) of the abdomen obtained after the administration of intravenous contrast show severe bowel wall thickening and pericolonic fat stranding involving the majority of the ascending and the entire transverse colon. Scattered mesenteric lymph nodes are noted. Infectious colitis Infectious colitis is caused by a variety of infectious agents and is described in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised or hospitalized patients. The lesions seen in these patients may be either superficial (similar to ulcerative colitis) or transmural (as in Crohn disease), diffuse (cytomegalovirus and Escherichia coli), predominantly right-sided (as seen in colitis caused by Yersinia, Salmonella, amebiasis, and tuberculosis), or mostly left-sided (schistosomiasis, shigellosis, herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, and lymphogranuloma venereum). Stool analysis, blood culture, and endoscopic biopsy are required for the diagnosis, as there is a considerable overlap in the CT appearance of these colitides.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree