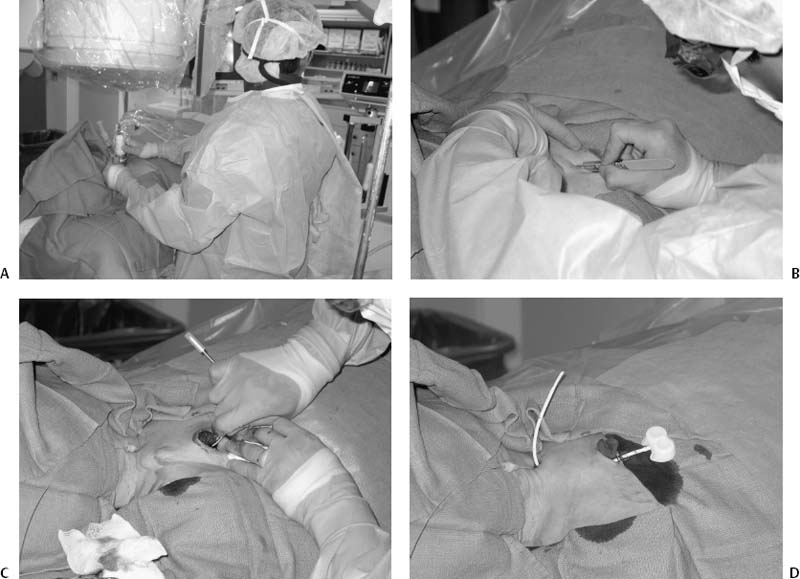
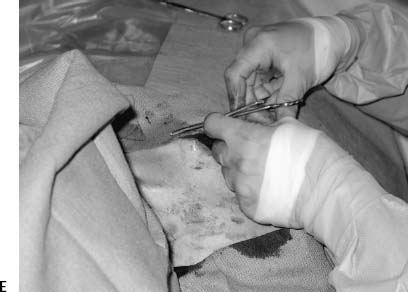
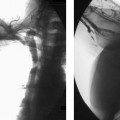
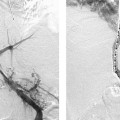
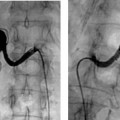
CASE 9 A 60-year-old female with colon cancer required central venous access for long-term, intermittent chemotherapy. What type of catheter is appropriate? Figure 9-1 Subcutaneous chest port insertion. (A) Sonographic right internal jugular vein puncture. Note strict adherence to sterile technique. (B) Incision is made into subcutaneous tissues of right anterior chest. (C) Tunnel is fashioned from incision in chest to puncture site in neck. (D) Assembled port with catheter portion pulled through tunnel to incision site in neck. (E) Final wound closure after port insertion. N/A A chest port would be the best catheter to insert. The patient was given 1 g of Cefizox (Astellas Pharma US, Inc.) immediately prior to the procedure. She was brought to the interventional radiology suite, and her skin was cleansed using a chlorhexidine solution. After subcutaneous administration of 1% lidocaine, the right internal jugular vein was punctured with a 21-gauge needle using sonographic guidance (Fig. 9-1A). The needle was exchanged over a 0.018-inch guidewire for coaxial 3F- and 5F-French (F) dilators. The 3F dilater was removed, and a guidewire was advanced from the puncture site into the inferior vena cava. A small subcutaneous pocket was created on the right anterolateral chest wall using sharp and blunt dissection (Fig. 9-1B). A tunnel was then made from the pocket to the puncture site in the neck using a tunneler included in the port access kit (Fig. 9-1C), and the catheter portion of the device was pulled through the tunnel (Fig. 9-1D). The catheter was then attached to the hub portion of the device, and the entire device was flushed with saline and inspected to confirm integrity of connections. The catheter was then cut to an appropriate length.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Studies
Diagnosis
Treatment
Chest Port Insertion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree