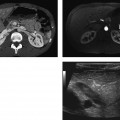
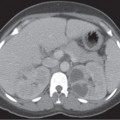
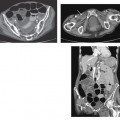
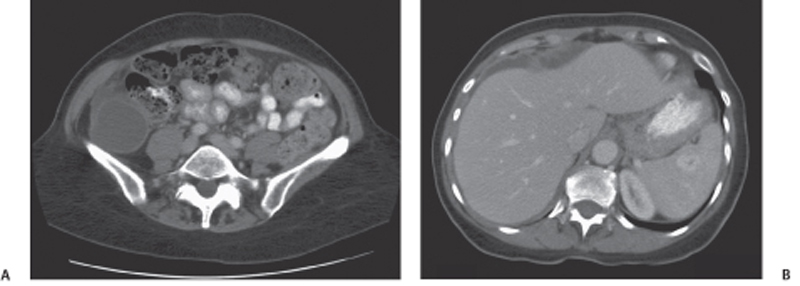
CASE 90 A 72-year-old woman presents with abdominal distention, fullness, and pain in the right iliac fossa. Fig. 90.1 (A) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows the presence of a cystic lesion with thick walls in the right iliac fossa with surrounding fat stranding and free fluid. (B) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image of the liver in the same patient shows scalloping of the liver margins and ascites with peritoneal thickening. Contrast computed tomography (CT) images show the presence of a cystic lesion in the right lower quadrant with ascites and scalloping of the liver margins (Fig. 90.1). Malignant mucocele of the appendix with pseudomyxoma peritonei Mucocele of the appendix is the accumulation of mucus with luminal distention of the appendix. The reported incidence is 0.2 to 0.5% of appendectomies. It can be benign or malignant. The benign variety results from occlusion of the appendiceal luminal opening into the cecum from a phlebolith or impacted feces. A malignant mucocele results from mucin-secreting adenocarcinoma of the appendix. Either a benign or a malignant mucocele can result in the development of pseudomyxoma peritonei on rupture.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree