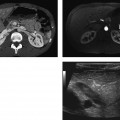
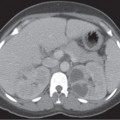
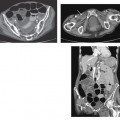
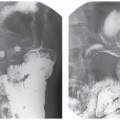
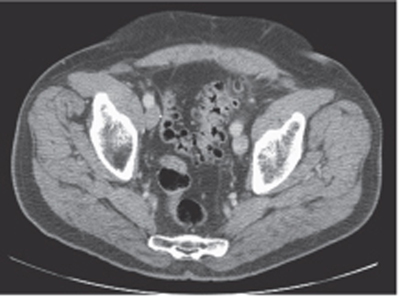
CASE 91 A 74-year-old man presents with lower abdominal pain and discomfort associated with a recent change in bowel habits. Fig. 91.1 An axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows diffuse diverticulosis, most significant in the sigmoid colon, with evidence of related mild muscular hypertrophy. No pericolonic inflammatory changes are noticed. An axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image (Fig. 91.1) shows diffuse diverticulosis, most significant in the sigmoid colon, with evidence of related mild muscular hypertrophy. No pericolonic inflammatory changes are noticed. Diverticulosis Diverticula are outpouchings of the intestinal walls, involving either all the layers (true diverticula) or just the mucosal and submucosal layers (false diverticula). Diverticular disease has been described anywhere in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract but is most frequently present in the sigmoid colon (95–98%) due to the higher segmental intraluminal pressures. These diverticula usually form through weaker points of the colonic walls, which represent the natural openings for the vasa recta and other nutrient vessels.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree