BI-RADS Categorization | ||
Clinical Findings | right 1 | left 3 |
Ultrasound | right 1 | left 3 |
Mammography | right 1 | left 3 |
MR Mammography | right 1 | left 3 |
BI-RADS Total | right 1 | left 3 |
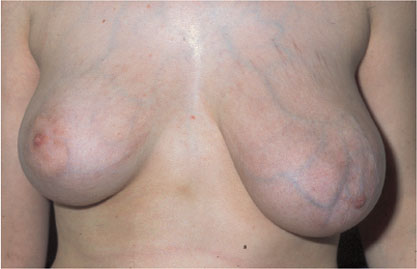
This young woman presented for further investigation of marked and escalating asymmetry, the left breast having increased considerably in size over the previous months.
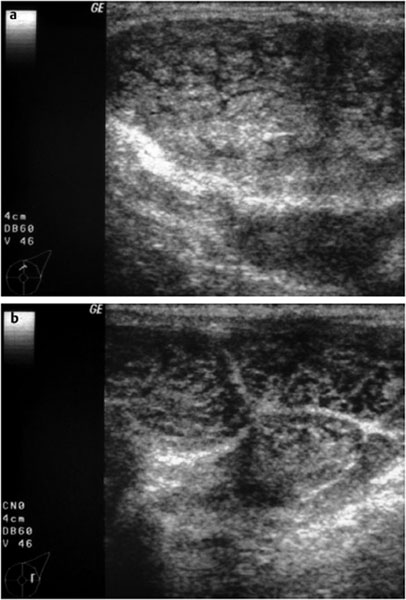
Ultrasound
Documentation of the entire lesion was impossible in sonography. Individual sections showed a conglomerate of multiple round, well-defined nodules with inhomogeneous, reticular internal structure. No cystic areas within the tumor. No unusual distal echo pattern. US BI-RADS left 3.
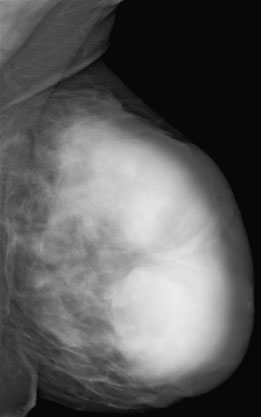
Mammography
Taking the extreme growth of the left breast into account, a digital MLO view was performed despite the youth of the patient. It was still considered necessary to exclude any signs of malignancy such as microcalcifications. As expected, mammography depicted a conglomerate of multiple homogeneous, well-defined, hyperdense lesions. No calcifications. BI-RADS left 3. PGMI is not defined for unilateral imaging.
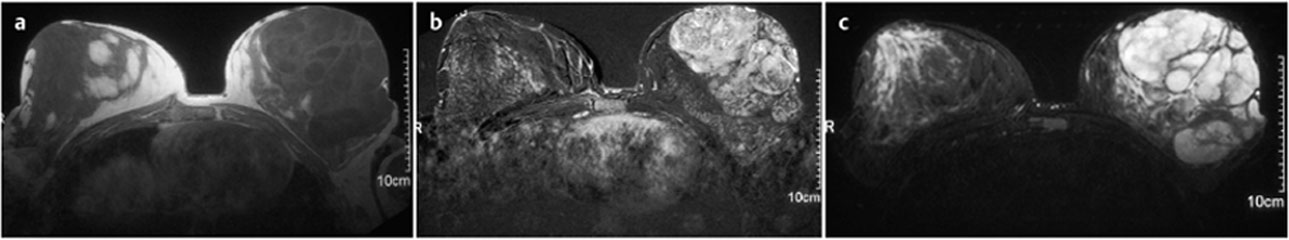
MR Mammography
MRI was performed as part of preoperative preparation. A massive hypervascularized conglomerate tumor was seen in the left breast. No signs of malignancy. The glandular tissue was displaced toward the chest wall by the tumor. BI-RADS left 3.
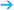 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Juvenile giant fibroadenoma (high probability); phyllodes tumor, sarcoma, lymphoma (low probability).
Procedure
The high probability of the tumor being benign was comprehensively explained to the young woman. On aesthetic and psychosocial grounds, resection of the tumor was recommended.
Histology
Giant fibroadenoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree