Case 95
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
A 40-year-old man with severe episodic hypertension.
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
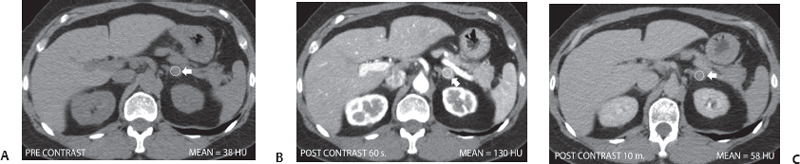
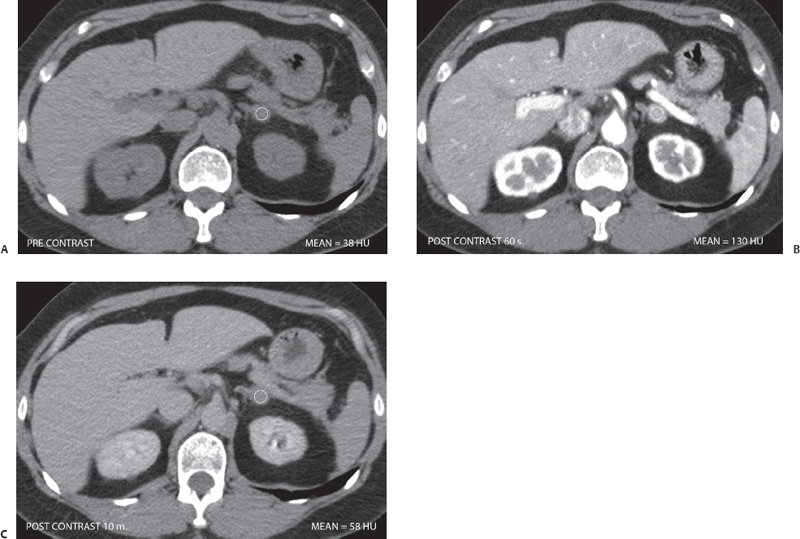
(A) Non–contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) at the level of the adrenal glands shows a nodule (arrow) in the left adrenal gland. It is well defined and homogeneous. The attenuation value is 38 Hounsfield units (HU). The right adrenal gland is normal. (B) Contrast-enhanced CT at the same level as that of Figure A obtained at 60 seconds shows marked homogeneous enhancement of the adrenal nodule (arrow), with an attenuation value measured at 130 HU. (C) Contrast-enhanced CT at the same level as that of Figure A obtained at 10 minutes shows significant washout of contrast from the left adrenal nodule (arrow), with a residual attenuation value of 58 HU. The absolute washout index is ~78%.
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Pheochromocytoma: Adrenal nodules that enhance to > 120 HU in the early phase should be considered pheochromocytomas, particularly if they show significant washout of contrast with a washout index similar to that of adenomas.
• Lipid-poor adrenal adenoma:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


