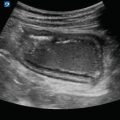
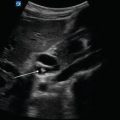
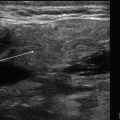
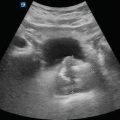
Figure 7.1
Transverse aorta: The normal aorta in transverse will be a circular structure with hyperechoic walls and a hypoechoic center (A), usually located directly anterior to the vertebral body (B) or just lateral to it. The IVC, sometimes collapsed, will be visualized to the patients right (C)
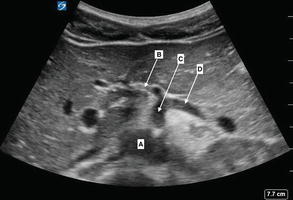
Figure 7.2
Celiac trunk with seagull sign: Arising from the aorta (A) is the celiac trunk (C), branching into the hepatic artery (B) and splenic artery (D)

Figure 7.3
Superior mesenteric artery: Superior mesenteric artery (A) is the second main branch from the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the celiac trunk

Figure 7.4
Renal arteries: Left (L) and right (R) renal artery branches

Figure 7.5
Aortic bifurcation: Near the umbilicus, the aorta will bifurcate into the right and left iliac arteries (arrows)

Figure 7.6
Sagittal aorta: Sagittal view of the aorta (A) at the level of the superior mesenteric artery (B) and celiac artery (C)
Image Acquisition
- (a)
Transducer Selection
Curvilinear
Phased array
- (b)
Patient Position
The patient should be placed in a supine position for optimal imaging.
If there is an excessive amount of bowel gas, left or right lateral decubital position can be utilized.
- (c)
Standard Exam Views
Transverse or cross-sectional imaging:
Place the transducer over the epigastrium just inferior to the xiphoid with the transducer marker pointed toward the patient’s right.
Keep the transducer perpendicular to the long axis of the aorta and follow the aorta down through the bifurcation at approximately the level of the umbilicus:
Figure 7.7—Transducer placement for imaging the aorta in a transverse plane
Sagittal imaging:
Place the transducer over the epigastrium with the transducer marker pointed cephalad.
Figure 7.8—Transducer placement for imaging the aorta in a sagittal plane.

Figure 7.7
Transducer placement for imaging the aorta in a transverse plane: Beginning just below the xiphoid process, scan the aorta from proximal to the distal bifurcation in a transverse orientation