103 Aliasing
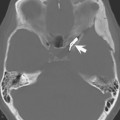
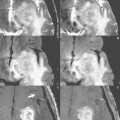
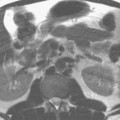
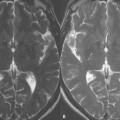
Figures 103.1 and 103.2 present examples of aliasing, defined as wraparound of structures outside a specified field of view (FOV) to the opposite side of the image. The phase-encoding direction is along the horizontal axis in Fig. 103.1 and along the vertical axis in Fig. 103.2. In Fig. 103.1A, a coronal postcontrast T1-weighted scan at 3 T (in a 5-year-old patient), the left side of the head is aliased to overlie the right side of the head and vice versa. Aliasing from the ears (white arrows, A) obscures both the low signal intensity portion (on the patient’s right) and the enhancing portion (on the patient’s left, black arrow, B) of this pontine glioma. In Fig. 103.2A, the neck is aliased to the top of the image (arrow). In Fig. 103.2C
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree