12 Approach and Techniques
Out-of-Plane Approach
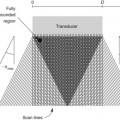
There are several advantages to the out-of-plane approach to regional block (Table 12-1). This approach is most similar to traditional approaches to regional block guided by nerve stimulation or palpation. Therefore, the out-of-plane approach provides a natural transition from one form of guidance to another. The out-of-plane approach uses a shorter needle path than in-plane approaches. If short-axis views of the nerve are used, an out-of-plane approach results in catheter placement that is guided along the path of the nerve. One disadvantage of the out-of-plane approach is the extent of the unimaged needle path (structures that may lie short of or beyond the scan plane). If the needle tip crosses the scan plane without recognition, it can be advanced beyond the scan plane into undesired tissue.
Table 12-1 Comparison of Out-of-Plane and In-Plane Approaches
| Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Out-of-plane (OOP) | Most similar to other approaches to regional block (nerve stimulation or palpation) Shorter needle path than with in-plane approaches Along the nerve path (catheters) | Unimaged needle path, crossing the plane of imaging without recognition |
| In-plane (IP) | Most direct visualization |