Arteries of the Lower Extremity
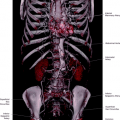
The common femoral artery is the continuation of the external iliac artery. It begins at the level of the inguinal ligament and ends when it originates the arteria profunda femoris. The continuation of the common femoral artery is then called the superficial femoral artery. The superficial femoral artery extends down the leg, where it passes through the adductor canal originating the popliteal artery (Figs. 22.1, 22.2, 22.3).
Knowledge of the vascular anatomy of the vessels in the groin and the relationship of the vessels with the femoral nerve is relevant for the current practice of medicine. Access to the arterial vascular system, including the abdominal aorta and the thoracic aorta and branches is mostly through femoral artery puncture. The femoral nerve (most lateral), the common femoral artery (in the center), and the common femoral vein (most medial) have a constant relationship when they pass under the inguinal ligament and reach the inguinal compartment, surrounded by muscles forming a bundle (Fig. 22.2). The common femoral artery is best palpated in the deepest fossa at the level of the inguinal crease.
Common Femoral Artery
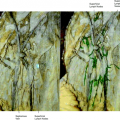
Intravascular ultrasound of the common femoral artery
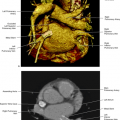
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) of a large artery such as the femoral artery shows the arterial wall structure in three layers: an inner echogenic layer, a middle hypoechoic layer, and an outer echogenic layer, histopathologically corresponding to the tunica intima, the tunica media, and the tunica adventitia. Next to the artery the femoral vein can be seen with a larger diameter and less well-defined layers (Fig. 22.4).
Branches
Superficial epigastric artery
Superficial circumflex iliac artery
Superficial external pudendal artery
Deep external pudendal artery
Arteria profunda femoris
Superficial femoral artery
Muscular branches
Descending genicular arteries
Superficial Epigastric Artery
This artery arises about 1 cm below the inguinal ligament and anastomoses with branches of the inferior epigastric artery and the opposite vessels (See Chapter 19, Fig. 19.1).
Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (Fig. 22.5)
Superficial External Pudendal Artery (Fig. 22.5)
Deep External Pudendal Artery (Fig. 22.5)
Muscular Branches
Arteria Profunda Femoris (Fig. 22.6)
Superficial External Pudendal Artery (Fig. 22.5)
Deep External Pudendal Artery (Fig. 22.5)
Muscular Branches
Arteria Profunda Femoris (Fig. 22.6)
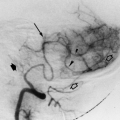
It is the largest branch of the femoral artery, with an origin about 3.5 cm from the inguinal ligament. It arises laterally and posteriorly from the femoral artery (Figs. 22.7, 22.8, 22.9, 22.10, 22.11, 22.12, 22.13, 22.14).
Branches
Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Ascending branch
Descending branch
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Perforating arteries. There are usually three (Fig. 22.7)
First perforating artery
Second perforating artery
Femoral nutrient artery
Third perforating artery
The end of the arteria profunda femoris is called the fourth perforating—numerous muscular branches are present at that level
Anastomoses
Gluteal arteries—with terminal branches of the medial circumflex femoral artery
Circumflex femoral arteries—with first perforating artery
Perforating arteries—communicating with each other
Fourth perforating artery—with superior muscular branches of popliteal arteries
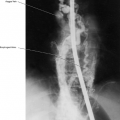
Descending Genicular Artery (Figs. 22.1, 22.15)
This artery branches from the superficial femoral artery before the adductor’s canal and anastomoses with the medial superior genicular artery.
Branches
Saphenous branch—anastomoses with medial inferior genicular artery
Muscular branches, articular branches
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is the continuation of the superficial femoral artery passing the adductor’s canal, continuing until branching into anterior and posterior tibial arteries (Figs. 22.15, 22.16, 22.17).
Branches
Cutaneous branches
Superior muscular branches
Sural arteries
Superior genicular arteries
Middle genicular artery
Inferior genicular arteries
Cutaneous Branches
Branches
Medial superior genicular artery
Anastomoses with descending genicular artery and medial inferior genicular artery
Lateral superior genicular artery
Anastomoses with the descending lateral circumflex, with the lateral inferior genicular artery, descending genicular artery, and medial superior genicular artery
This artery is small and not always recognizable.
Branches
Medial inferior genicular artery
Anastomoses with the lateral inferior genicular artery, the medial superior genicular artery, the anterior tibial recurrent artery and the saphenous branch, and the descending genicular artery.
Lateral inferior genicular artery
Anastomoses with the medial inferior genicular artery, the lateral superior genicular artery, and anterior and posterior tibial recurrent circumflex peroneal arteries.
Genicular Anastomosis (Figs. 22.15, 22.22)
Superficial Network
Fascia
Skin
Fat
Deep Network
Articular surface
Bone
Marrow
Capsule
Synovial membrane
Participating Vessels
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree