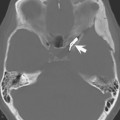
66 Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) Imaging: Applications
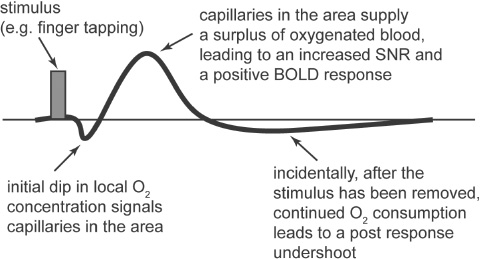
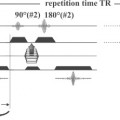
Fig. 66.1
Variations in magnetic susceptibility induced by an increase in oxygenation within a localized area are very minute, as is the resulting SNR increase. To visualize the effect during an MRI measurement, the patient is asked to perform a series of tasks during the sequence acquisition to induce an alternating increase and decrease in the levels of oxyhemoglobin to a specific area of the brain. This increase and decrease follows a well-known pattern called the hemodynamic response function (Fig. 66.1).
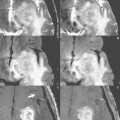
The tasks are performed in a cycle called a paradigm specified in the sequence parameters prior to the sequence acquisition. By synchronizing the data acquisition and activity paradigm to the hemodynamic response within the brain, images can be acquired and sorted to depict the area of activation. For example, Fig. 66.2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree