10 10.1 Mammographic features of breast lesions 10.2 Calcification Examples of definitely benign calcification: 10.4 Benign lesions with typical appearances 1. Fibroadenoma – rounded, lobulated, well-defined homogeneously dense soft-tissue opacity with eccentrically sited ‘pop-corn’ calcification. 2. Intramammary lymph node – well-defined, approximately 1.0 cm in diameter soft-tissue opacity, often with an eccentric radiolucency situated most often in the upper outer quadrant of the breast. 3. Lipoma – large, rounded, radiolucent, well-defined. 4. Lipid cyst – well-defined, multiple, lucent, ‘egg-shell’ calcification. 5. Hamartoma/fibroadenolipoma – ‘breast within a breast’ appearance on a mammogram. 10.5 Single well-defined soft-tissue opacity 3. Intramammary lymph node – intramammary lymph nodes occur in up to 40% of breasts. Causes include breast cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, regional inflammation/dermatitis, fungal infection, tuberculosis/granulomatous disease, foreign body reactions, e.g. gold injections for rheumatoid arthritis, silicone adenopathy, HIV and sinus histiocytosis. 1. Cystosarcoma phylloides – usually large, may be benign but have malignant potential (5–10%), calcification rare, median age 45–49, rare < 30 or > 60. High tendency to recur, both in benign and malignant. Malignant lesions metastasize to lung and bone and may invade chest wall. 2. Carcinoma – a small group of carcinomas looks ‘benign’ on mammography; medullary, encephaloid, mucoid, papillary. 10.6 Multiple well-defined soft-tissue opacities 2. Fibroadenomas – 10–20% are multiple. 3. Skin lesions – e.g. neurofibromas. 5. Metastases – melanoma most common, lymphoma second most common non-mammary breast tumour, then lung, ovarian, soft-tissue sarcomas, gastrointestinal/genitourinary malignancy, carcinoid and sporadically thyroid, osteosarcoma, cervical, vaginal and endometrial. Mean survival after diagnosis of metastasis within the breast is < 1 year.
Breast disease and mammography
Lesion characteristics
Benign
Malignant
Opacity
Smooth margin
Ill-defined margin, stellate
Speculate, comet tail
Low density
High density
Homogeneous
Inhomogeneous
Thin ‘halo’
Wide ‘halo’
Calcification (see 10.3)
±
±
Surrounding parenchyma
Normal
Disrupted
Nipple/areola
± Retracted
± Retracted
Skin
Normal
± Thickened
Cooper ligaments
Normal
May be thickened/increased
Ducts
Normal
Focal dilatation
Subcutaneous/retromammary space
Normal
± Obliterated
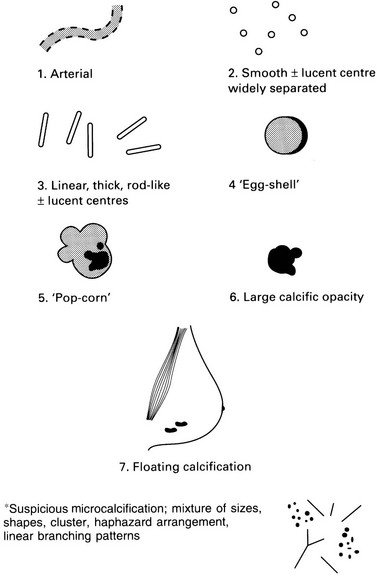
Definitely benign (see figure, p. 247)
Probably benign
Suspicious of malignancy
Arterial, tortuous, tramline (1)
Smooth, widely separated radiolucent centre (2)
Linear, thick, rod-like ± radiolucent centre (3)
Egg-shell, curvilinear margin of cyst, fat necrosis (4)
Pop-corn (fibroadenoma) (5)
Large individual > 2 mm (6)
Floating, seen on lateral oblique, milk of calcium cysts (7)
Widespread, both breasts
Macrocalcification of one size
Symmetrical distribution
Widely separated
Superficial distribution
Normal breast parenchyma
Microcalcification, segmental*
Pleomorphic, linear, branching, punctuate*
Associated suspicious soft-tissue opacity
Eccentrically located in soft-tissue mass
Deterioration on serial mammography
Benign
Malignant
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Breast disease and mammography