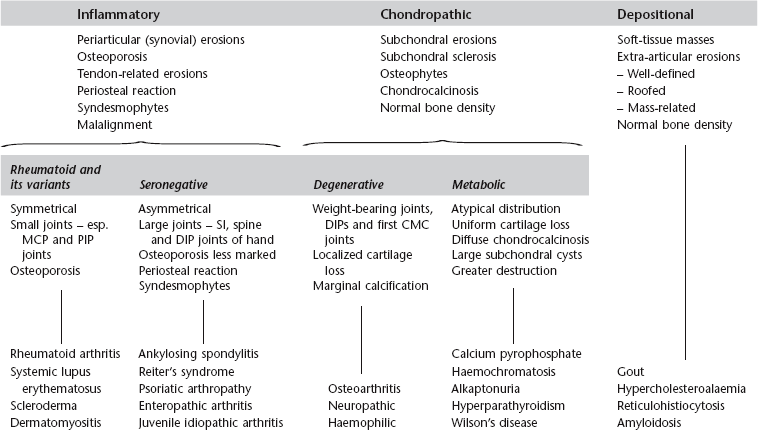
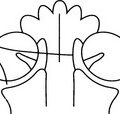
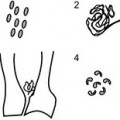
3 3.1 Monoarthritis 1. Trauma – pointers to the diagnosis are: (a) the history, (b) the presence of a fracture, and (c) a joint effusion, especially a lipohaemarthrosis. 4. Rheumatoid arthritis* – occasionally. Also juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 5. Pyogenic arthritis – commonest joints affected are the hip, knee and small joints of the hands and feet. 15% of those due to Staphylococcus aureus and 80% of those of gonococcal aetiology involve two or more joints. The joint may be radiographically normal at first presentation. 6. Tuberculous arthritis – insidious onset with radiological changes present at the time of first examination. Erosions first develop at peripheral non-contact points of the joint. 7. Pigmented villonodular synovitis* – most commonly at the knee. 8. Sympathetic – a joint effusion can occur as a response to a tumour in the adjacent bone. Demertzis, J. L., Rubin, D. A. MR imaging assessment of inflammatory, crystalline-induced, and infectious arthritides [Review]. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011; 19(2):339–363. Murphey, M. D., Vidal, J. A., Fanburg-Smith, J. C., Gajewski, D. A. Imaging of synovial chondromatosis with radiologic–pathologic correlation [Review]. Radiographics. 2007; 27(5):1465–1488. 3.3 Arthritis with osteoporosis 2. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 3. Systemic lupus erythematosus*. 6. Reiter’s syndrome* – in the acute phase. 3.4 Arthritis with preservation of bone density 2. Calcium pyrophosphate arthropathy – see Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease*. 6. Reiter’s syndrome* – in chronic or recurrent disease. 7. Neuropathic arthropathy* – especially in the spine and extremities. 3.5 Arthritis with a periosteal reaction 1. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis*. 5. Rheumatoid arthritis* – in less than 5% of patients. 6. Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy. 3.6 Arthritis with preserved or widened joint space 1. Early infective or inflammatory arthritis – because of joint effusion. 2. Psoriatic arthropathy* – due to deposition of fibrous tissue. 3. Acromegaly* – due to cartilage overgrowth. 3.7 Arthritis with soft-tissue nodules
Joints
Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine