“Bump” thought to represent aberrant clava, used as marker for cervicomedullary junction
 Abnormal tonsillar “pistoning” motion, reduced CSF flow around foramen magnum and cerebellar tonsils
Abnormal tonsillar “pistoning” motion, reduced CSF flow around foramen magnum and cerebellar tonsils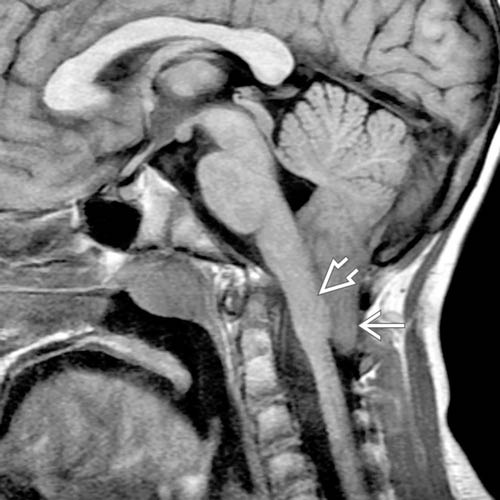
 and inferior displacement of the obex
and inferior displacement of the obex  . The 4th ventricle is in normal position.
. The 4th ventricle is in normal position.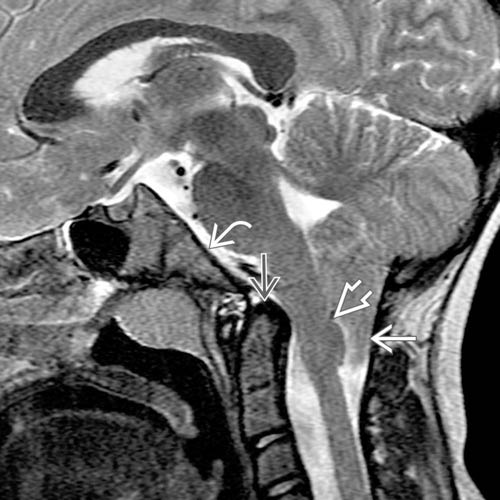
 and inferior displacement of the cervicomedullary junction, marked by position of the obex
and inferior displacement of the cervicomedullary junction, marked by position of the obex  below the foramen magnum. There is also mild retroflexion of the odontoid process
below the foramen magnum. There is also mild retroflexion of the odontoid process  and mild clivus
and mild clivus  foreshortening.
foreshortening.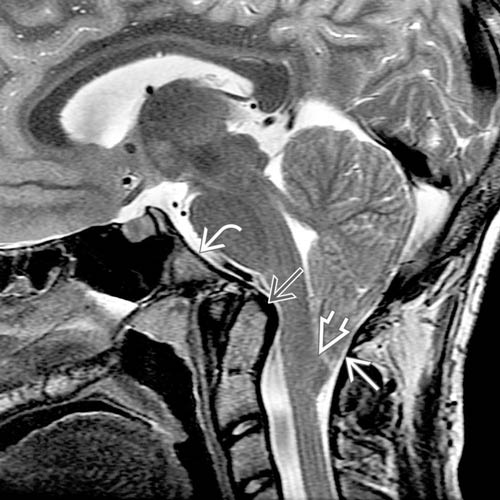
 and pointed, ectopic cerebellar tonsils
and pointed, ectopic cerebellar tonsils  . The odontoid process
. The odontoid process  is retroflexed and the clivus
is retroflexed and the clivus  is foreshortened, with a reduced craniocervical angle with platybasia.
is foreshortened, with a reduced craniocervical angle with platybasia.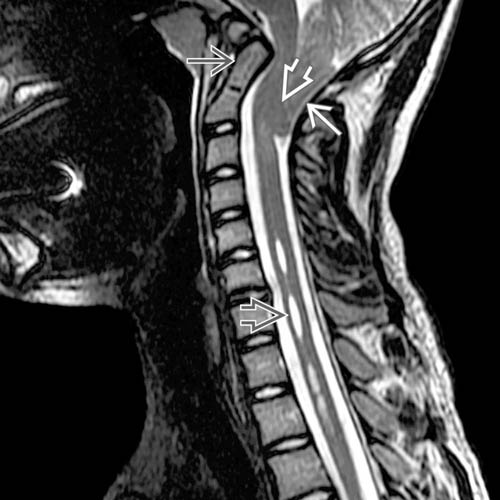
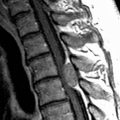
 retroflexion. Note also severe cerebellar tonsillar ectopia
retroflexion. Note also severe cerebellar tonsillar ectopia  extending inferiorly to the C3 level and cervical syringohydromyelia
extending inferiorly to the C3 level and cervical syringohydromyelia  . The prominent, inferiorly displaced obex
. The prominent, inferiorly displaced obex  confirms a complex Chiari malformation.
confirms a complex Chiari malformation.IMAGING
General Features
• Best diagnostic clue




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree