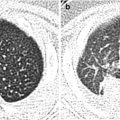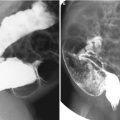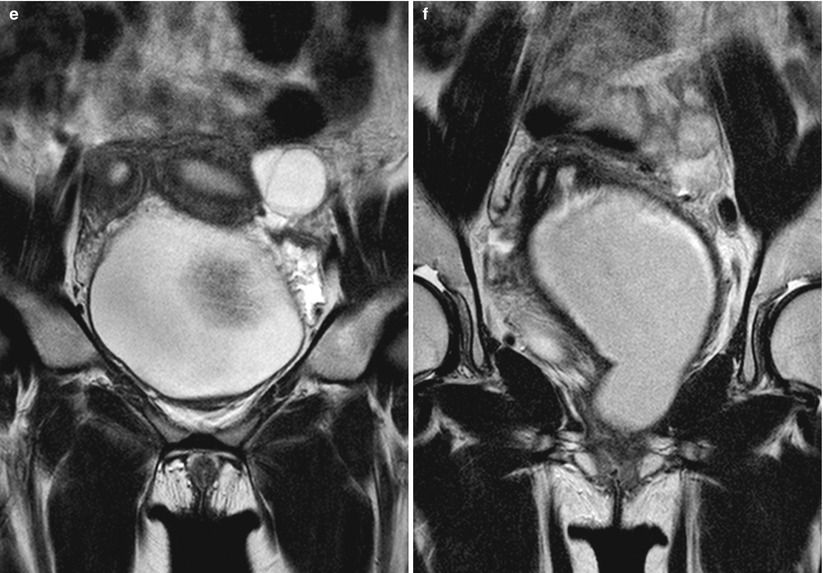
Fig. 23.1
Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich syndrome in a 15-year-old girl. (a–d) Abdominopelvic CT of axial (a and b) and coronal (c and d) images show double uterus (arrows) with distended left hemivagina (arrowhead) due to obstruction. Left kidney is not visualized in left abdomen. (e and f) T2-weighted coronal MR images also well demonstrate uterine didelphys with left vaginal obstruction
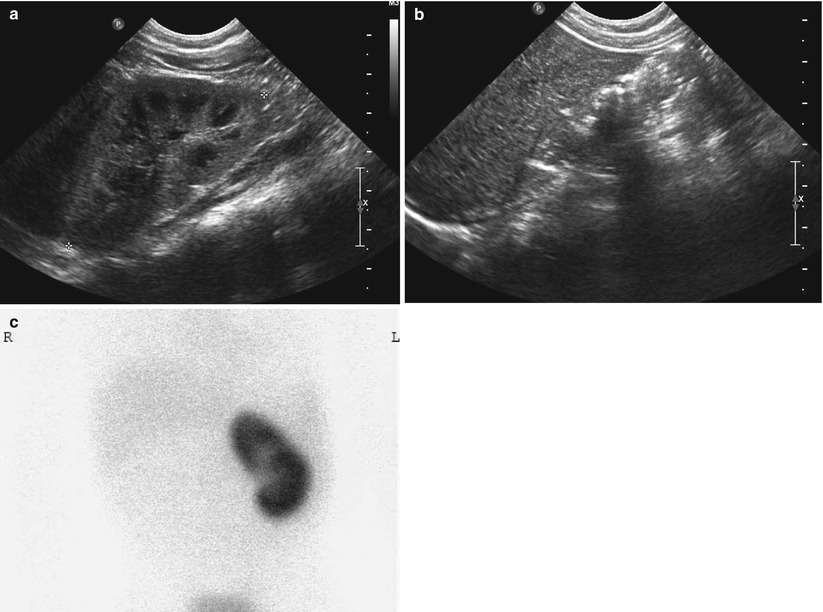
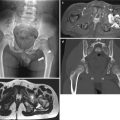
Fig. 23.2
Renal agenesis in a 3-year-old boy. (a) Abdominal US of left abdomen shows hypertrophied left kidney. (b) Right kidney is not seen in right renal fossa. (c) Tc-99 m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan shows grossly normal left kidney and nonvisualized right kidney
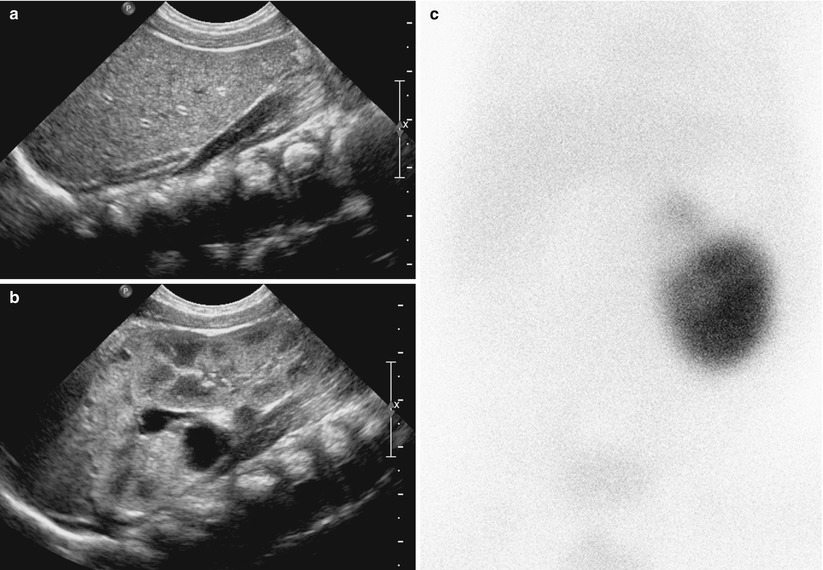
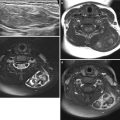
Fig. 23.3
Renal agenesis with contralateral duplex collecting system in a 3-month-old girl. (a) Right kidney is not seen in right renal fossa on abdominal US. (b) Abdominal US of left abdomen shows duplex collecting system of left kidney with multiple small cortical cysts and pelvic dilatation in upper pole. (c) Tc-99 m DMSA scan shows decreased uptake in the dysplastic upper pole of left kidney and nonvisualized right kidney
23.4.2 Anomalies of Kidney: Anomalies of Form – Renal Hypoplasia
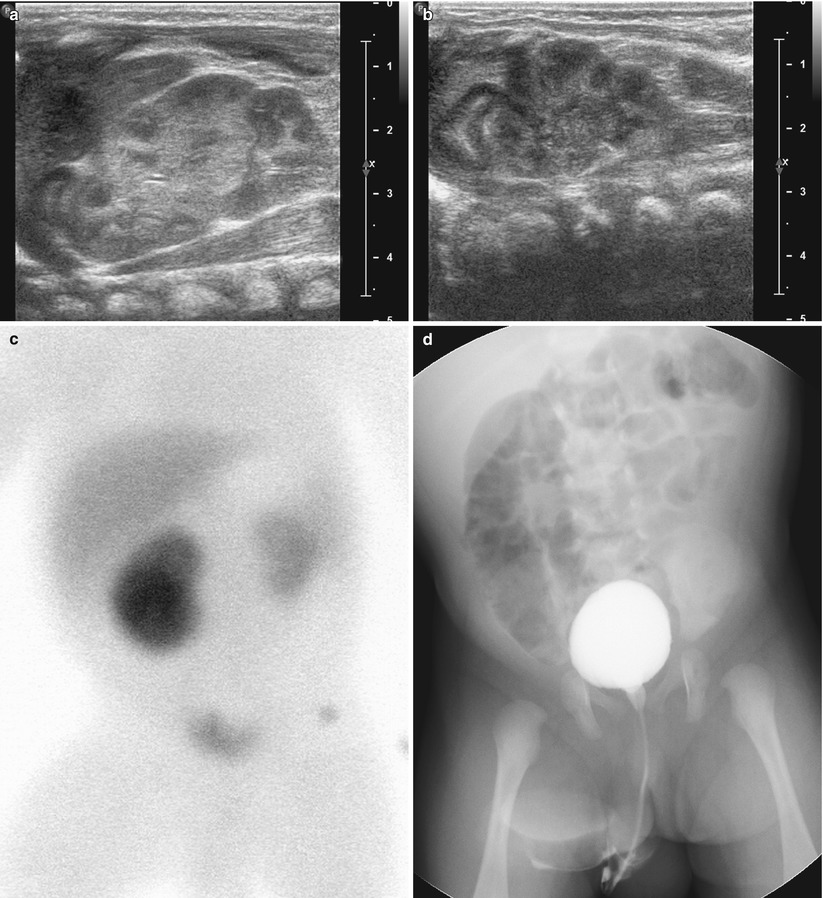
Fig. 23.4
Renal hypoplasia in a 2-month-old boy. (a and b) Abdominal US images show grossly normal right kidney (a) and relatively small left kidney (b) without other focal lesion. (c) Tc-99 m DMSA scan shows decreased uptake in the relatively small left kidney. Split renal function was calculated to be 83 % on the right kidney and 17 % on the left kidney. (d) Voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) demonstrates no vesicoureteral reflux
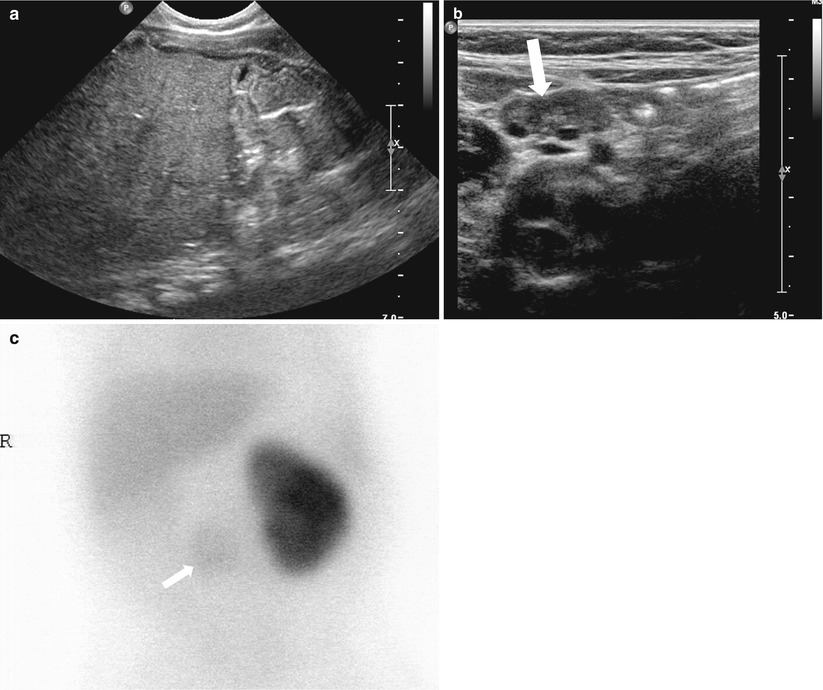
Fig. 23.5
Ectopic hypoplastic kidney in a 6-month-old boy. (a) Right kidney is not visualized in right renal fossa on abdominal US. (b) A small dysplastic kidney (arrow) with cortical cysts is noted in prevertebral area of mid abdomen on abdominal US. (c) Tc-99 m DMSA scan shows faint uptake (arrow) in the hypoplastic kidney
23.4.3 Anomalies of Kidney: Anomalies of Rotation
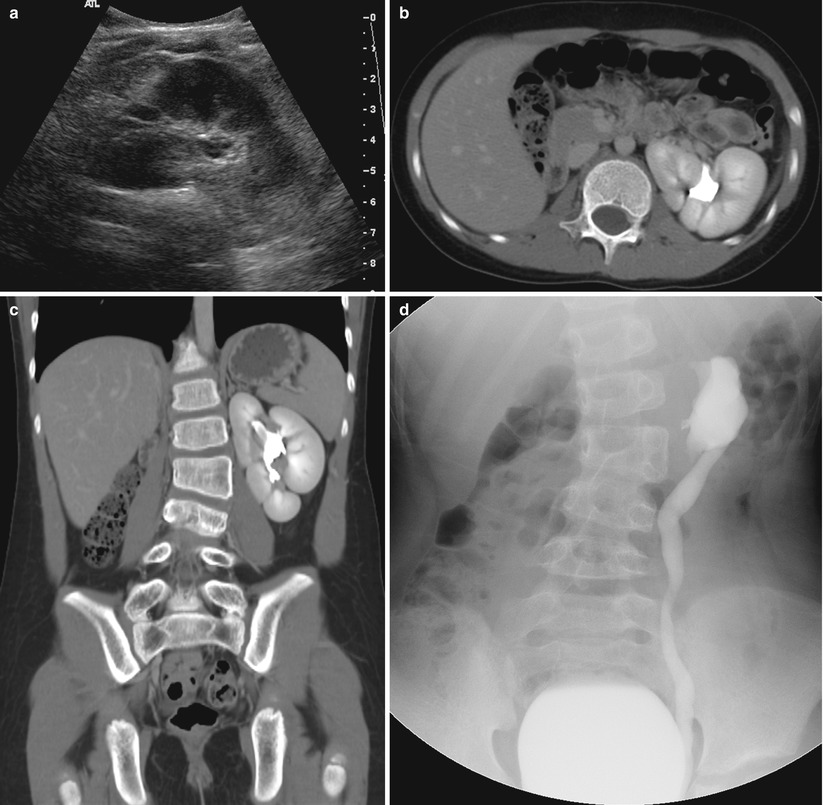
Fig. 23.6
Renal malrotation in a 9-year-old girl. (a) Left kidney shows fetal lobulation with incomplete rotation in left upper abdomen on abdominal US. (b and c) Axial (b) and coronal (c) images of abdominopelvic CT also show anterior position of left renal pelvis. (d) VCUG demonstrates left vesicoureteral reflux with anterior position of renal pelvis
23.4.4 Anomalies of Kidney: Anomalies of Position
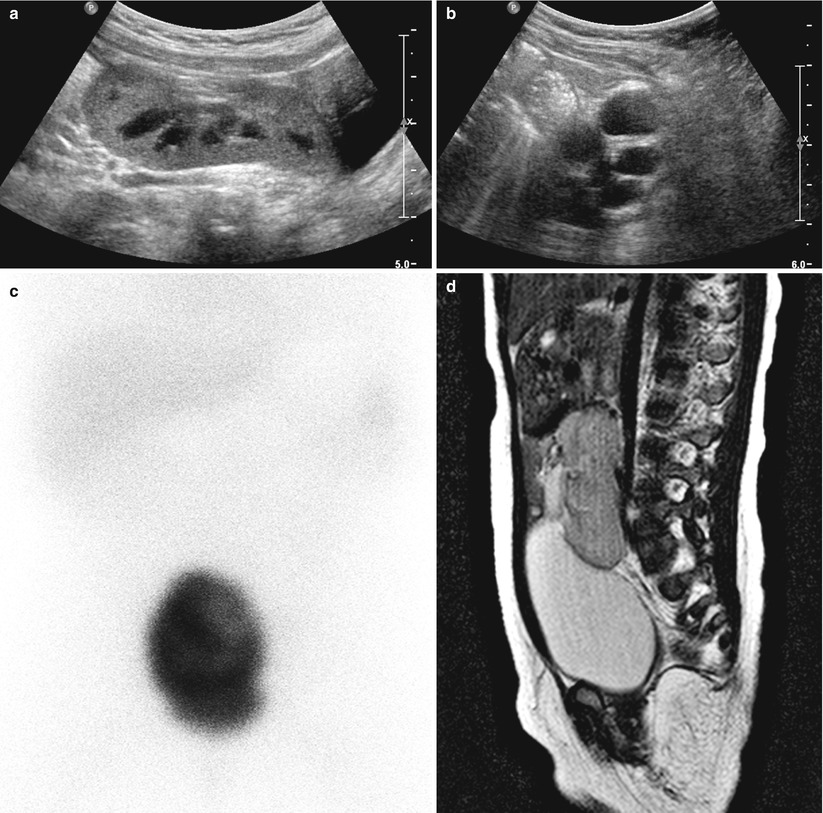
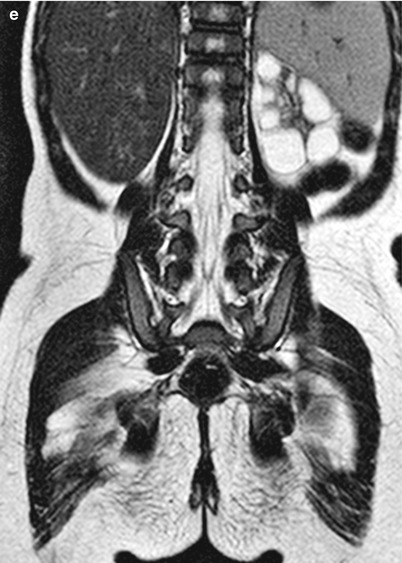
Fig. 23.7
Pelvic kidney in a 1-year-old boy. (a) Abdominal US shows hypertrophied right kidney in pelvic cavity just above urinary bladder with anterior position of renal pelvis. (b) Abdominal US of left renal fossa shows multicystic dysplastic left kidney. (c) Tc-99 m DMSA scan shows only uptake in the pelvic kidney. (d) T2-weighted sagittal MR image shows right pelvic kidney just above urinary bladder with pelvic dilatation. (e) T2-weighted coronal MR image shows multicystic dysplastic left kidney in left renal fossa and nonvisualized right kidney in right renal fossa
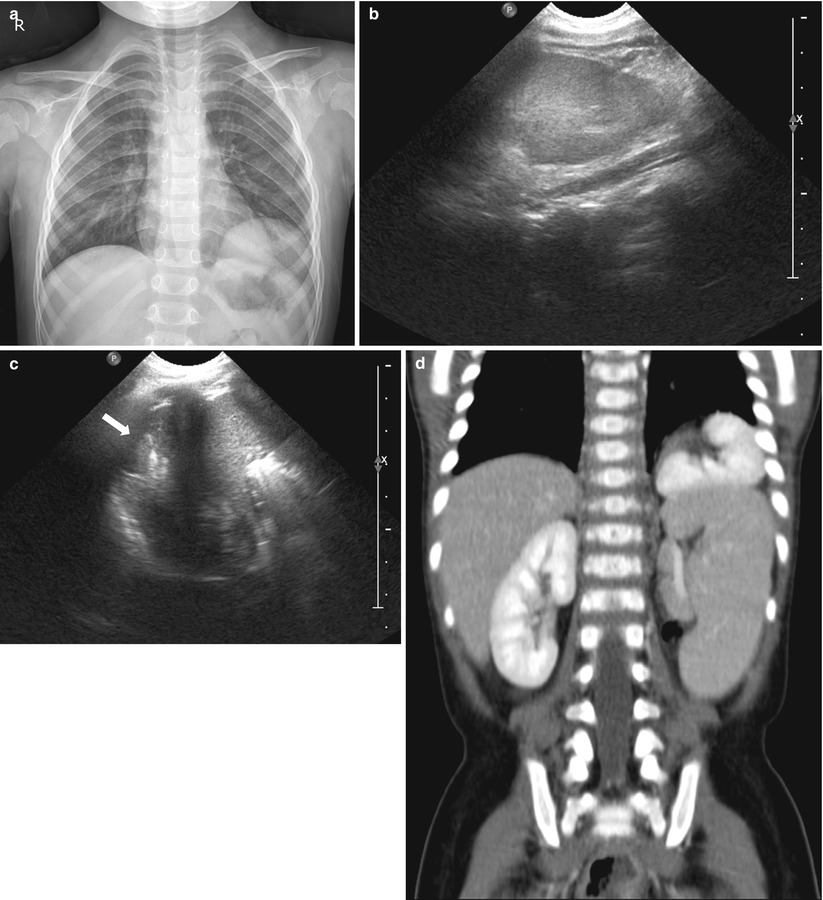
Fig. 23.8
Thoracic kidney in a 2-year-old girl. (a) Chest X-ray shows incidentally found mass lesion in left lower thorax. (b and c) On abdominal US, left kidney is not visualized in left renal fossa (b), and soft tissue lesion (arrow) is defined above the spleen (c). (d) Abdominal CT shows thoracic kidney above the spleen in left lower thorax
23.4.5 Anomalies of Kidney: Anomalies of Fusion – Horseshoe Kidney
Fig. 23.9
Horseshoe kidney in a male neonate with imperforate anus. (a) Abdominal US of mid-transverse abdomen shows the isthmus (fused portion) of horseshoe kidney anterior to aorta and crossing midline. (b) T2-weighted axial MR image shows horseshoe kidney with functional renal parenchyma at isthmus. (c) Tc-99 m DMSA scan also demonstrates functioning tissue at isthmus
23.4.6 Anomalies of Kidney: Anomalies of Fusion – Crossed Fused Ectopy
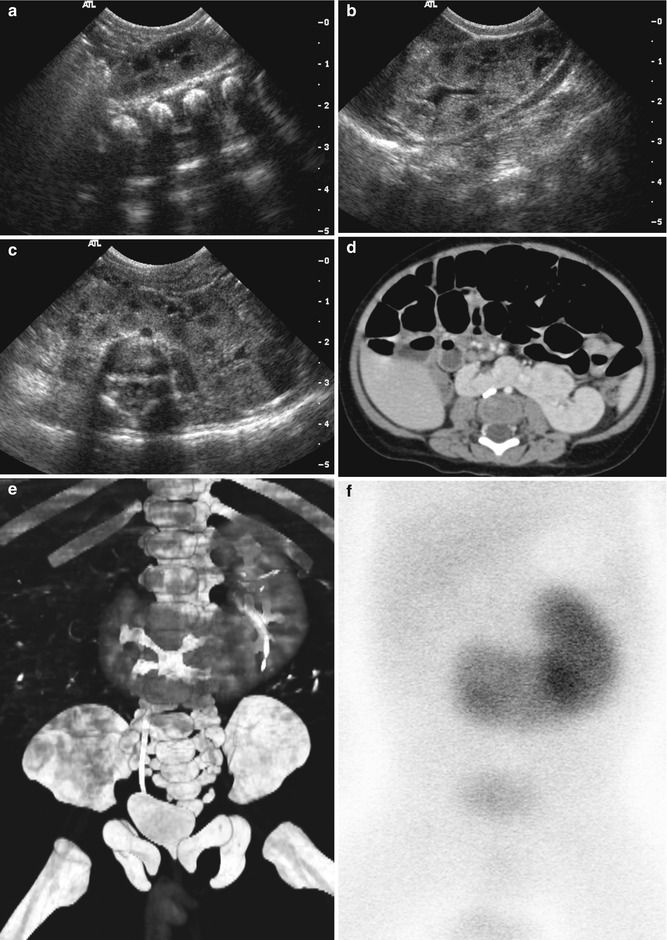
Fig. 23.10
Crossed fused ectopy in a 5-month-old boy. (a) Abdominal US of right renal fossa shows relatively small volume of right kidney. (b) US image of left abdomen shows grossly normal left kidney in left renal fossa. (c) Transverse US image of mid abdomen demonstrates fused portion of kidney anterior to aorta. (d) Contrast-enhanced CT scan of mid abdomen shows crossed ectopy of right kidney in midline lower abdomen and noncrossing left kidney with fusion. (e) Three-dimensional reconstruction image of contrast-enhanced CT scan well demonstrates the unilateral fused type with inferior ectopy in this patient. (f) Tc-99 m DMSA scan also demonstrates crossed fused ectopy of right kidney
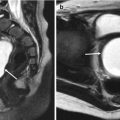
23.4.7 Anomalies of Renal Calyces: Calyceal Diverticulum
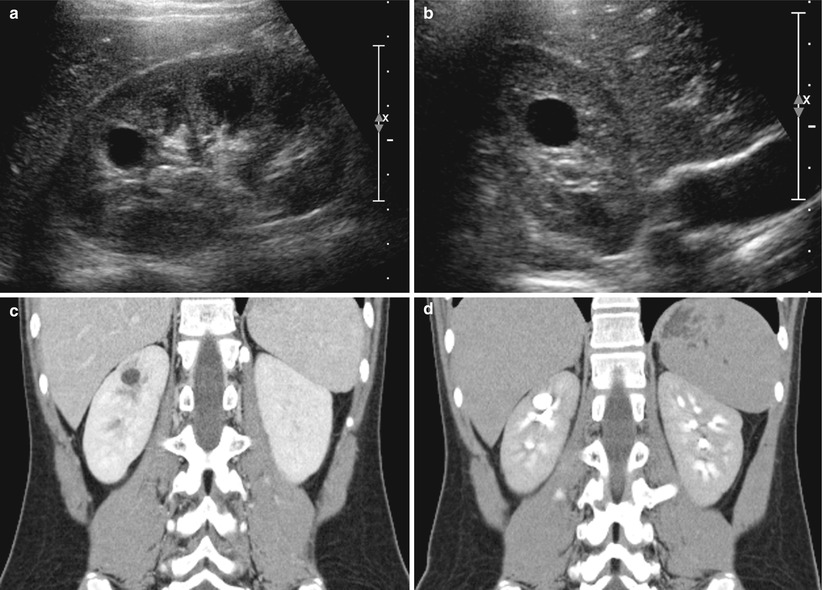
Fig. 23.11




Calyceal diverticulum in an 11-year-old girl. (a and b) Sagittal (a) and axial (b) images of right kidney on US show well-defined cystic lesion in the medullary portion of upper pole without visible connection with renal collecting system. (c) Contrast-enhanced CT scan of nephrographic phase also shows cystic lesion in right kidney upper pole. (d) CT scan of excretory phase demonstrates contrast material excretion into the cystic lesion, a finding that represents a calyceal diverticulum
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree