This patient has a large rounded opacity arising from the upper aspect of the right hilum (arrowheads). CT of the chest followed by bronchoscopy and biopsy led to a tissue diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer
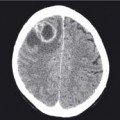
14.2 Metastatic disease
This patient has a widened mediastinum due to lymph node enlargement and numerous small well-defined rounded lung nodules. These are typical features of metastatic disease
14.3 Lung cavity
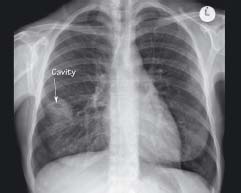
A lung shadow shows a central lucency due to formation of a cavity. This patient had an infected embolus originating from the femoral vein where the patient had injected intravenous drugs
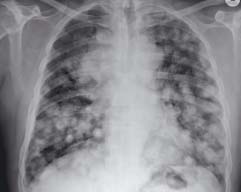
14.4 Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
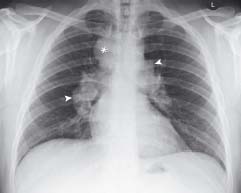
Both hila are enlarged (arrowheads). There is also enlargement of the mediastinum in the region of right paratracheal edge (*). These are classic appearances of sarcoidosis
14.5 Apical scarring due to TB
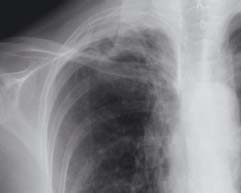
At the lung apex there is irregular fibrotic shadowing. The hilum has been pulled upwards due to volume loss. These features of old TB are often accompanied by calcification
14.6 Thoracic aortic aneurysm
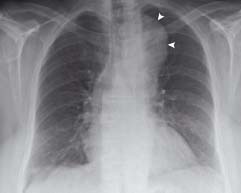
The left side of the aortic arch is enlarged with a smooth contour (arrowheads) due to aneurysmal dilatation of the thoracic aorta
Lung cancer
Approximately 10% of patients with lung cancer are asymptomatic and diagnosed incidentally on CXR. Primary lung cancer is the foremost cause of cancer-related mortality in both men and women. Its prevalence is second only to prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women. The lungs have a rich vascular and lymphatic network, which also predisposes them as a site for metastatic cancer. Cancers that frequently metastasise to the lung include thyroid, breast, kidney, prostate, melanoma and bone cancer.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree