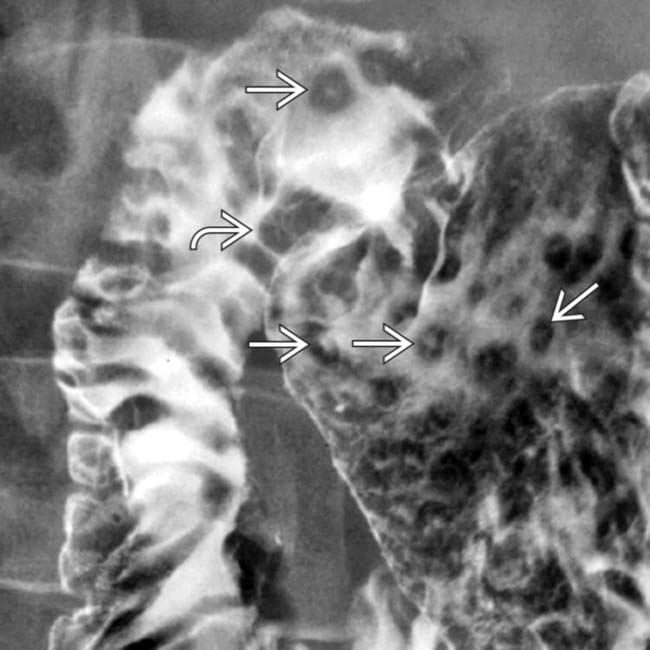
 in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds
in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds  , classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.
, classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.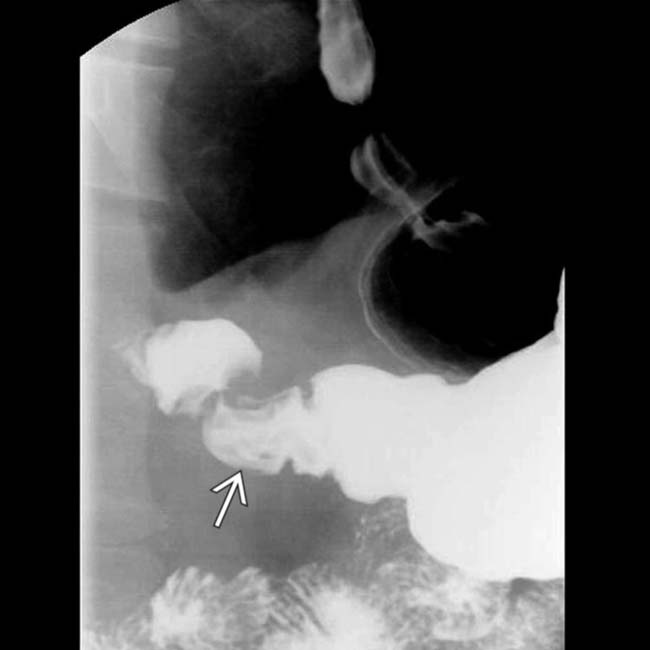
 and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.
and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.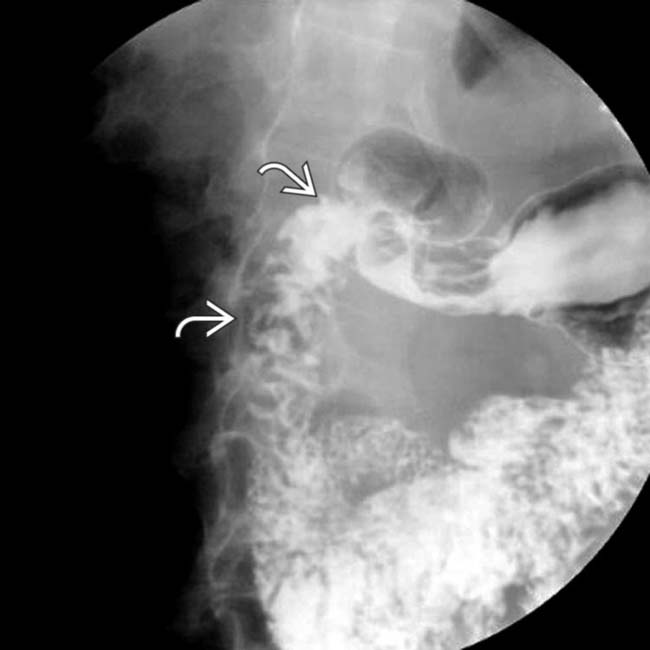
 , due to duodenitis.
, due to duodenitis.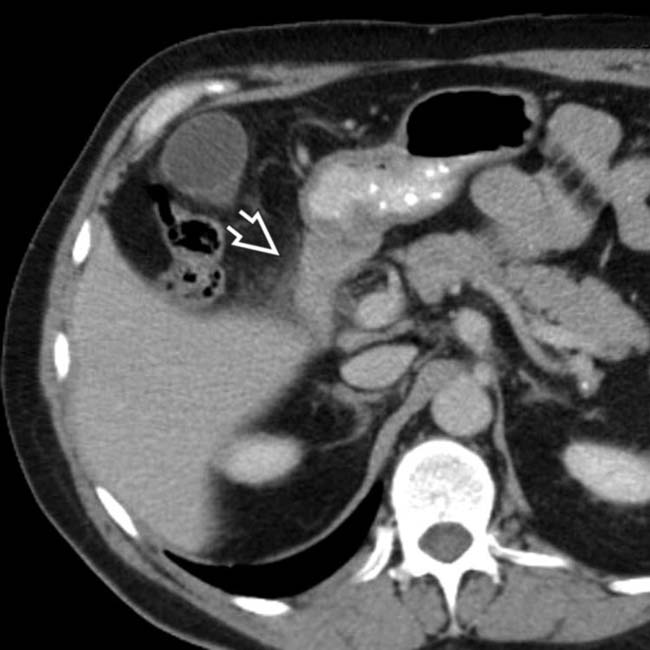
 due to duodenitis.
due to duodenitis.IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings


















