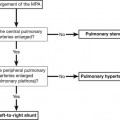
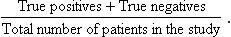15 1. Reliability – reproducibility of results. (These may be from the same observer or from different observers.) Assessment of this can be built into a study of diagnostic accuracy of a technique, or evaluated beforehand. 2. Accuracy: ‘proportion of results (positive and negative) which agree with the final diagnosis’, i.e. 3. Sensitivity – ‘proportion of diseased patients who are reported as positive’, i.e. 4. Specificity – ‘proportion of disease-free patients who are reported as negative’, i.e.
Evaluating statistics – explanations of terminology in general use
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine