8 Evaluation of Nerves of the Elbow and Forearm
Evaluation of Pronator Syndrome
♦ Setup
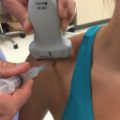
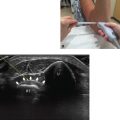
• The patient should be seated beside the operator with the forearm in supination resting on the table (Fig. 8.1).
• The elbow should be slightly flexed for patient comfort.
• A standard linear probe or narrower probe should be used.

Fig. 8.1 Left forearm in supination, elbow slightly flexed.
♦ Landmarks
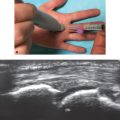
The following landmarks should be noted (Fig. 8.2):
• Medial epicondyle (ME)
• Biceps tendon (BiT)
• Pronator teres (PT)
• Flexor carpi radialis (FCR)
• Brachioradialis (BR)

Fig. 8.2 Surface anatomy of the elbow and forearm: medial epicondyle (asterisk), biceps tendon (black line), brachioradialis (Br), pronator teres (PT), and flexor carpi radialis (FCR).
♦ Probe Positioning
• The brachioradialis can be gently retracted laterally to further expose the PT and separate it from the FCR.
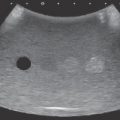
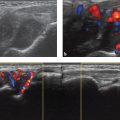
• The probe should be positioned at 90 degrees to the long axis of the forearm (Fig. 8.3).
• The probe should be placed between the ME and BiT.
• The median nerve is medial to brachial artery.
• The patient should gently pronate the forearm and then flex the wrist to confirm the location of the PT versus the FCR.

Fig. 8.3 Left forearm. (a) The probe is positioned 90 degrees to the long axis of the forearm between the medial epicondyle (ME) and biceps tendon (BiT). (b) Axial view. The arrow indicates the median nerve; the arrowheads indicate the bicipital aponeurosis (lacertus fibrosus). A, Brachial artery; B, brachialis; PT, pronator teres. (See Video 8.1.)
♦ Normal Anatomy

Fig. 8.4 shows the normal anatomy of the median nerve as it courses through the elbow and forearm:
• Medial epicondyle (ME)
• Ligament of Struthers
• Pronator teres (PT)
• Bicipital aponeurosis (lacertus fibrosus)
• Brachial artery
• Median nerve
• Arch of flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis arch)
♦ Pathology in Pronator Syndrome
• Entrapment of the median nerve between the superficial and deep heads of the PT
• Entrapment beneath the bicipital aponeurosis (lacertus fibrosus)
• Entrapment beneath the flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis bridge)
• Entrapment more proximally at an anomalous ligament of Struthers
Fig. 8.4 Normal anatomy of the median nerve as it courses through the elbow and forearm.
♦ Injection
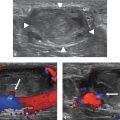
• Injection should be performed using a 12 MHz linear probe.
• A shallow injection angle is necessary.
• Injection should follow in-plane with the probe.
• Approach should be medial to lateral.
• A 25-gauge 1.5-inch needle is used to inject 1 ml of 1% lidocaine mixed with 1 mL of 40 mg/mL methylprednisolone into the fascial plane surrounding the median nerve (Fig. 8.5).
• The brachial artery and BiT must be avoided.

Fig. 8.5 (a) Medial to lateral in-plane approach. (b) Axial view. Injection is made into the fascial plane surrounding the median nerve (arrow). The brachial artery must be avoided.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree