, Joungho Han2, Man Pyo Chung3 and Yeon Joo Jeong4
(1)
Department of Radiology Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of (South Korea)
(2)
Department of Pathology Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of (South Korea)
(3)
Department of Medicine Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of (South Korea)
(4)
Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea, Republic of (South Korea)
Abstract
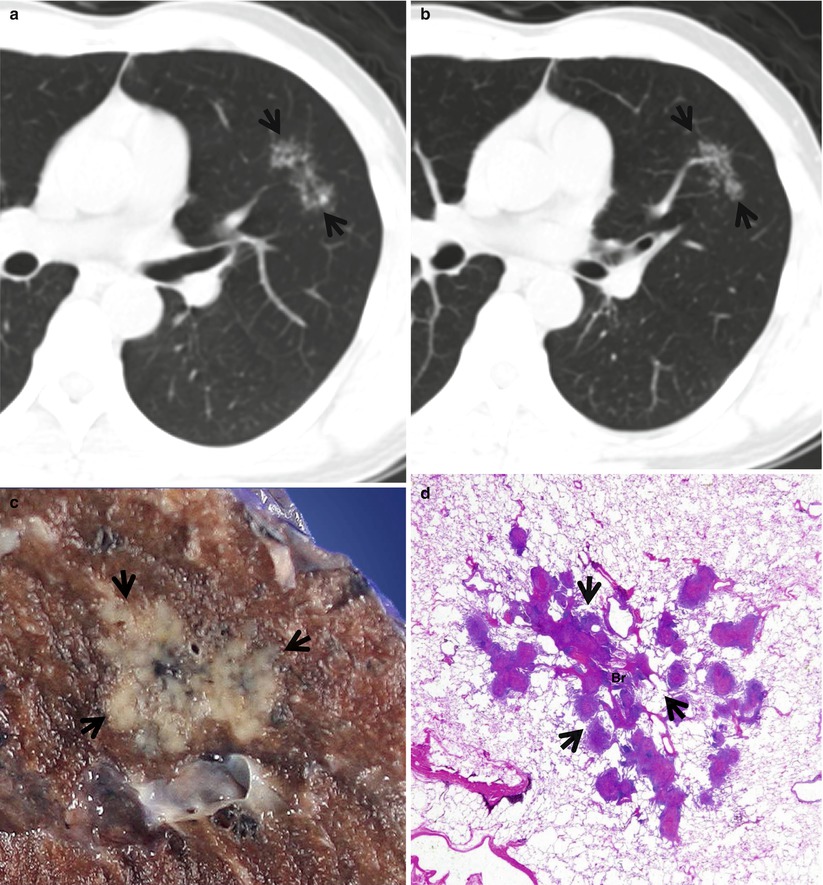
A large pulmonary nodule composed of multiple small nodules and surrounded by many very smaller satellite nodules is called a galaxy sign [1] (Fig. 7.1).
Definition
A large pulmonary nodule composed of multiple small nodules and surrounded by many very smaller satellite nodules is called a galaxy sign [1] (Fig. 7.1).
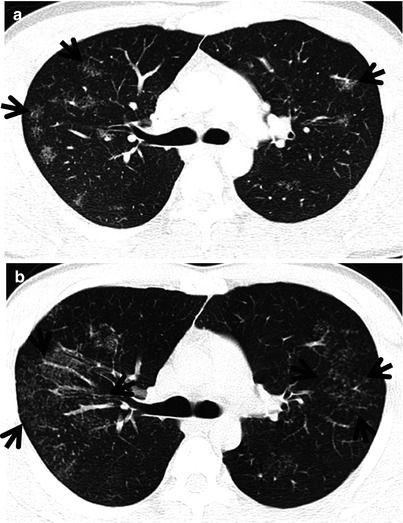

Fig. 7.1
CT galaxy sign in a 23-year-old man with pulmonary sarcoidosis. (a, b) Consecutive thin-section (2.5-mm section thickness) CT scans obtained at levels of the right upper lobar bronchi show multifocal areas of CT galaxy sign (arrows) that are comprised of multiple small nodules and surrounded by many very small satellite nodules, particularly in the right upper lobe. Mediastinal window images (not shown here) demonstrated enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum and hilum, bilaterally
Diseases Causing the Sign
The nodule(s) with CT galaxy sign is (are) observed in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis and active pulmonary tuberculosis [2] (Table 7.1) (Figs. 7.2 and 7.3).
Table 7.1
Common diseases manifesting as galaxy sign
Disease | Key points for differential diagnosis |
|---|---|
Sarcoidosis | Associated with lymphadenopathy |
Pulmonary tuberculosis | Associated with tree-in-bud pattern, upper lung predominance |