Heart and Great Vessels: The Great Vessels
In young children, the great vessels, on conventional radio-graphs, are or can be obscured by the shadow of the thymus. As the thymus diminishes in size, the great vessels become more and more visible.
Imaging of the great vessels will mostly be done using CT and/or MRI. The use of diagnostic angiography should be considered to be obsolete.
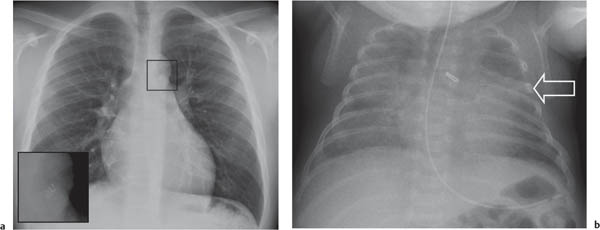
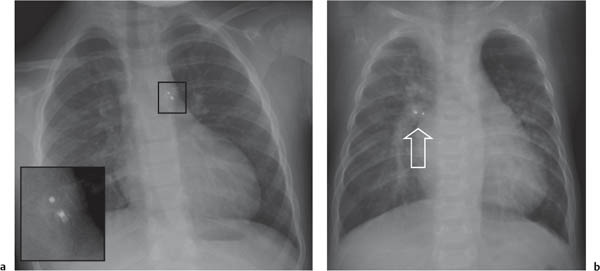
Coronary Artery Disease
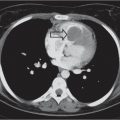
Compared to adults, coronary artery disease in children is a rare finding; however, with the advent of modern imaging techniques, the pediatric radiologist should be aware of the pathology of coronary arteries.
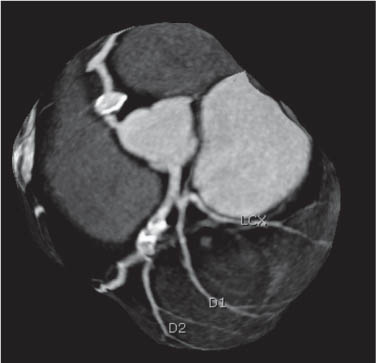
D1 | First diagonal branch of LAD |
D2 | Second diagonal branch of LAD |
LCX | Left circumflex artery |
Rings and Slings
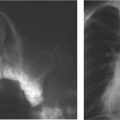
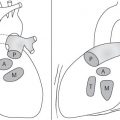
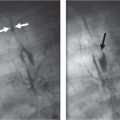
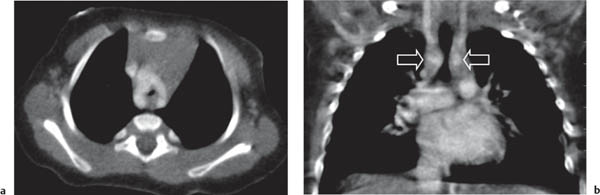
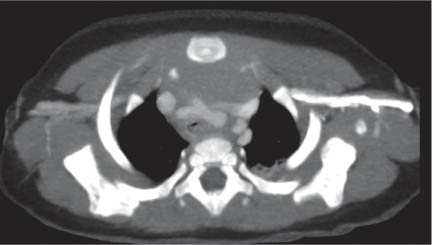
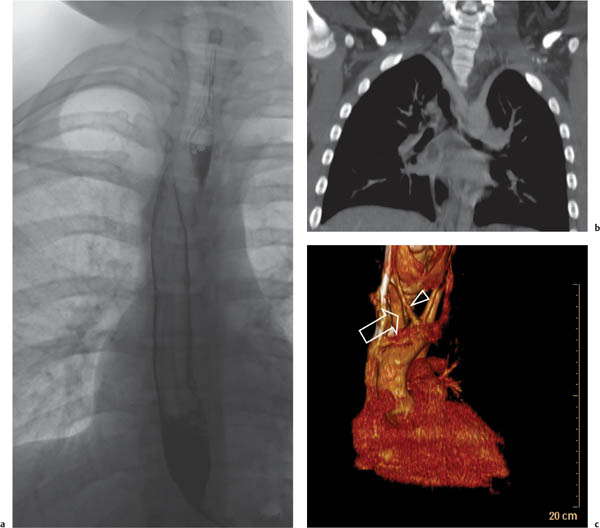
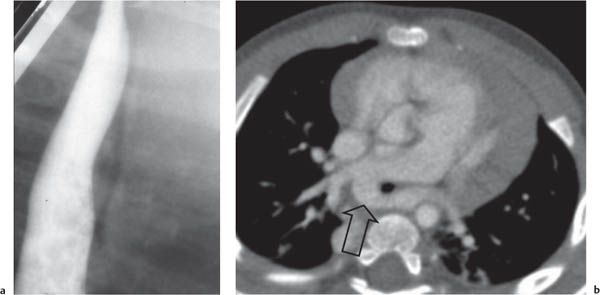
A vascular ring is the result of anomalous development of the aortic arch. In the embryologic stage, the aorta forms a ring around the primitive foregut, and anomalous development leads to an aortic ring or sling.
Historically, the primary diagnostic tool was the contrast (barium) swallow; however, with the advent of CT and MRI, this technique has been superseded and should be considered obsolete.
In young children, the main presenting symptom may be stridor, often the result of concomittant tracheomalacia. Later in life, dysphagia is the most common symptom.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree