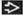Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Triad characterized by
Chronic liver disease (usually cirrhosis)
Increased alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient on room air (> 15 mmHg)
Intrapulmonary vascular dilatation
Imaging Findings
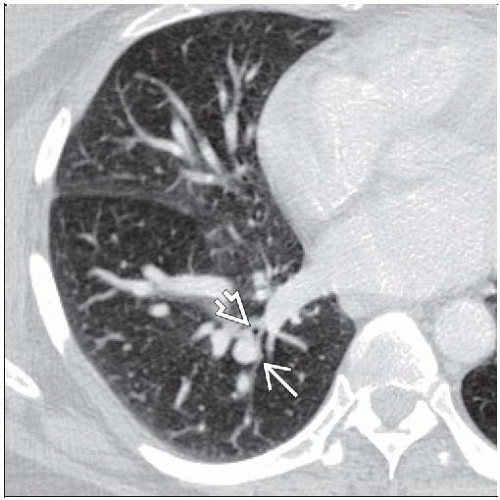
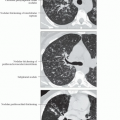
Best imaging finding: Dilated peripheral arteries on CT
Arterial bronchus ratio in periphery usually > 2
MIP reconstructions or thick sections better depict vascular abnormality than HRCT
Nuclear medicine: Macroaggregated albumin bypasses lungs and results in systemic activity in brain and kidneys
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pulmonary Artery Hypertension
Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation
Intravascular Metastases
Pathology
No correlation between hypoxemia in HPS and severity of liver disease (Child classification)
Clinical Issues
Dyspnea presenting symptom in 20%
Platypnea 90%: Dyspnea in upright position, relieved with supine position
Reversible after orthotopic liver transplantation (80%) (20% do not improve)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary alveolar-arterial gradient = PAO2-PaO2
Definitions
Triad characterized by
Chronic liver disease (usually cirrhosis)
Increased alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient on room air (> 15 mmHg)
Intrapulmonary vascular dilatation
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Dilated peripheral arteries (2x larger than adjacent bronchi) on CT
Patient position/location: Lower lobes
Size: Arterial bronchus ratio in periphery usually > 2
CT Findings
Peripheral arteries dilated (artery larger than accompanying bronchus)
Normal bronchoarterial relationship
1:1, arterial diameter = bronchial diameter
Arteries may be slightly larger in dependent lung (1.2 ± 0.2) due to gravity
HPS ratio typically (2.0 ± 0.2)
Pulmonary artery diameter inversely correlated with PaO2
MIP reconstructions or thick sections better depict vascular abnormality than HRCT
Peripheral arteries may extend to pleural surface
Normally arteries become invisible 5-10 mm from pleural surface
Enlarged main pulmonary artery
Cirrhosis
Nodular liver contour, small liver, relative hypertrophy of left hepatic lobe
Splenomegaly
Esophageal or gastric varices
Ascites
Comorbid conditions, especially centrilobular emphysema or pleural effusions (from ascites or hypoproteinemia) common
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
May be normal
Main pulmonary artery may be enlarged
Mild cardiomegaly
Small nodular opacities in bases from dilated vessels
Seen in 5% with cirrhosis, 50% of those with proven HPS
Lung volumes normal (or enlarged if coexisting COPD)
Portal hypertension associated findings
Splenomegaly
Ascites
Small right or bilateral pleural effusions
Retrocardiac paraspinal widening from varices
Nuclear Medicine Findings
V/Q scan
Macroaggregated albumin bypasses lungs and results in systemic activity in brain and kidneys
Normal pulmonary capillary diameter 8-15 µm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree